Mapping Technology Market Set to Exceed $20.63 Billion by 2025: Growth in the U.S., South Korea, and the U.K.
Explore the rapidly growing Mapping Technology Market, projected to exceed $20.63 billion by 2025, with strong growth in the U.S., South Korea, and the U.K.
- Last Updated:
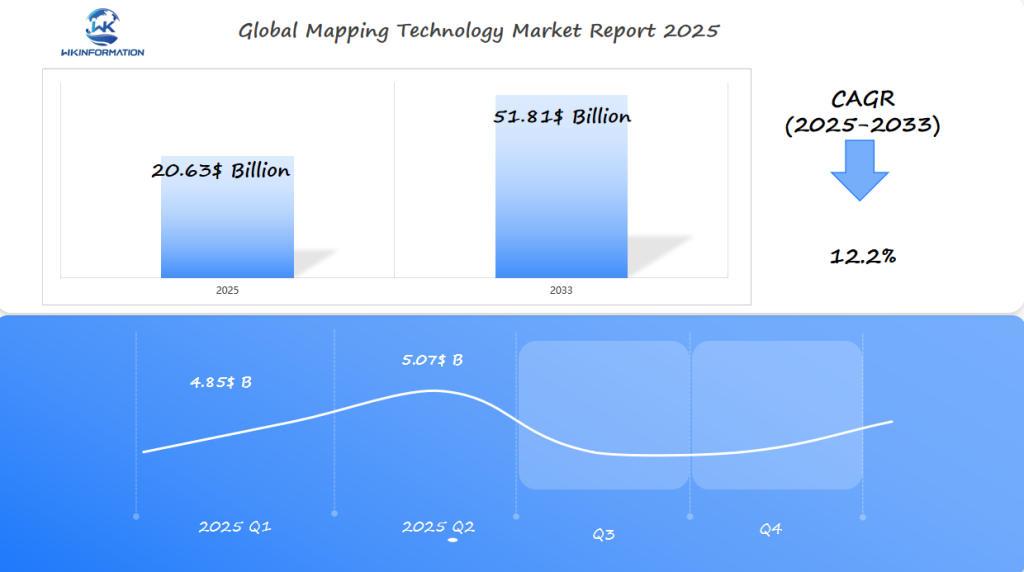
Mapping Technology Market in Q1 and Q2 of 2025
The Mapping Technology market is expected to reach $20.63 billion in 2025, growing at a steady rate of 12.2% from 2025 to 2033. In the first quarter of 2025, the market size is projected to be around $4.85 billion, with the second quarter potentially reaching $5.07 billion.
Factors Driving Market Growth
Several factors are driving the growth of the mapping technology market:
- Rapid urbanization: The increasing population and urban development require efficient mapping solutions for planning and infrastructure management.
- Drone-based surveying: Drones are being widely used for aerial mapping, providing cost-effective and accurate data collection.
- Smart city initiatives: Governments are implementing smart city projects that involve advanced mapping technologies for transportation management and urban planning.
Regional Insights
Here’s a glimpse into how different regions are contributing to the mapping technology market:
- United States: The U.S. remains the largest market for mapping technology, with applications in defense intelligence and autonomous navigation.
- South Korea: South Korea continues to invest in 3D mapping solutions for traffic systems and urban planning purposes.
- United Kingdom: The U.K. government is promoting public access to geospatial data, which can be used for planning and climate analysis.
Technological Advancements
Integration with various technologies is enhancing the capabilities of mapping solutions:
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LiDAR technology is being used to capture highly detailed elevation data, improving the accuracy of maps.
- Machine learning: Machine learning algorithms are being applied to analyze large datasets and extract meaningful insights from maps.
- Satellite imagery: Satellite images provide a broader perspective for mapping applications, enabling monitoring of land use changes and environmental impacts.
These advancements are creating new opportunities for businesses in the mapping technology industry.
Upstream and Downstream Value Chain of Mapping Technology
The value chain of mapping technology includes many activities, starting from gathering data to using it in applications. This intricate process involves different parties and technologies, resulting in the production of comprehensive maps utilized in various sectors.
Understanding the Value Chain
The value chain consists of two main segments: upstream and downstream.
Upstream Segment
The upstream segment focuses on data collection through advanced technologies such as LIDAR, GPS, and photogrammetry. These technologies enable the capture of precise geographical data, which is then processed and refined.
Downstream Segment
The downstream segment involves the application of this collected data in various fields, including autonomous vehicles, urban planning, and environmental monitoring. The integration of mapping data in these areas enhances their functionality and efficiency.
Trends in autonomous vehicles, drones, and geospatial data analytics
The combination of autonomous vehicles, drone technology, and geospatial data analytics is changing how we think about mapping and navigation. This partnership is not only improving the accuracy and effectiveness of different industries but also creating new opportunities for creativity and expansion.
Autonomous Vehicles and Mapping
Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on high-definition (HD) maps for navigation. These maps provide detailed information about the environment, including lane markings, traffic signals, and other critical data necessary for safe and efficient travel. The integration of HD maps with sensor data enables autonomous vehicles to make informed decisions in real-time, significantly improving their operational capabilities.
Key benefits of HD mapping for autonomous vehicles include:
- Enhanced safety through precise navigation
- Improved route optimization
- Increased efficiency in data processing
Drone Mapping Technologies
Drone mapping technologies are being increasingly utilized for aerial surveys, monitoring, and inspection tasks. Equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors, drones can capture detailed imagery and data, which are then used to create accurate 3D models and maps. This technology is particularly valuable in construction, agriculture, and environmental monitoring.
The advantages of drone mapping include:
- Cost-effectiveness compared to traditional aerial survey methods
- Rapid data acquisition and processing
- High precision in data collection
Geospatial data analytics plays a crucial role in interpreting the vast amounts of data collected from various sources, including autonomous vehicles and drones. By analyzing this data, industries can gain valuable insights, make informed decisions, and drive strategic initiatives forward.
Restrictions related to data accuracy, integration, and infrastructure costs
Despite advancements in mapping technology, issues related to data accuracy, integration, and infrastructure costs remain.
The importance of data accuracy cannot be overstated, particularly in applications like autonomous vehicles, where incorrect data can have significant consequences.
Challenges in Data Accuracy
Ensuring data accuracy is a complex task that involves collecting and processing vast amounts of data from various sources. The challenge is made more difficult by factors such as environmental conditions, sensor limitations, and the need for real-time processing.
- Inaccurate data can lead to incorrect mapping, which can have serious implications for applications like autonomous vehicles.
- The cost of achieving high data accuracy can be prohibitively expensive, requiring significant investments in technology and personnel.
Infrastructure costs are another significant challenge facing the mapping technology sector. Updating and maintaining mapping systems requires substantial investment, which can be a barrier to adoption for some organizations. Furthermore, integration issues arise when combining mapping data with other technologies, requiring seamless interoperability.
| Challenge | Description | Impact |
| Data Accuracy | Inaccurate data collection and processing | Incorrect mapping, safety risks |
| Infrastructure Costs | High costs of updating and maintaining mapping systems | Barrier to adoption, financial strain |
| Integration Issues | Difficulty combining mapping data with other technologies | Seamless interoperability challenges |

Geopolitical considerations for cross-border mapping data sharing and privacy laws
Data Sovereignty and National Security
-
Countries are increasingly treating geospatial data as a strategic asset, restricting foreign access due to its implications for military, infrastructure, and economic planning.
-
Nations like China, Russia, and India enforce strict localization laws that prevent sensitive mapping data from being stored or processed outside their borders.
Divergent Privacy and Data Protection Laws
-
EU (GDPR): Treats location data as personal data. Sharing across borders requires strict adherence to consent and anonymization protocols.
-
U.S.: Has sectoral regulations (e.g., CCPA in California), but lacks a comprehensive federal law, leading to more open commercial use of mapping data.
-
China: Implements the Data Security Law and Cybersecurity Law, with heavy state control over map data distribution, especially involving foreign entities.
Regulatory Fragmentation and Compliance Risk
-
Companies operating globally must navigate inconsistent rules around spatial data accuracy, resolution limits, and approved sources.
-
In some countries, only state-approved basemaps can be used, posing operational and legal risks for foreign firms or cloud-based GIS providers.
Restrictions on High-Resolution Satellite and Drone Mapping
-
Export controls and national laws often restrict the resolution or frequency of geospatial imagery that can be shared internationally.
-
For example, U.S. satellite firms must comply with NOAA and DoD restrictions, while India and China have tight controls on aerial mapping by private or foreign actors.
Type segmentation: LIDAR, GPS, photogrammetry, and radar mapping technologies
Mapping technologies like LIDAR, GPS, photogrammetry, and radar are transforming industries with their unique capabilities. The mapping technology market can be segmented based on the type of technology used, each with its own set of applications and advantages.
LIDAR Mapping Technology
LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology is known for its high accuracy in creating detailed 3D models of environments. It uses laser light to measure distances, making it invaluable for applications such as autonomous vehicles, urban planning, and environmental monitoring.
The precision of LIDAR technology allows for the creation of highly detailed topographic maps, which are crucial for various industries, including construction and forestry.
GPS and Photogrammetry Mapping
GPS (Global Positioning System) technology is widely used for navigation purposes, providing location information and timing information. It’s essential for mapping applications that require precise location data.
Photogrammetry involves creating maps from photographs taken from various angles. This technique is particularly useful for creating detailed maps of areas that are difficult to access or survey using traditional methods.
Both GPS and photogrammetry are critical components of the mapping technology ecosystem, offering unique benefits and applications across different industries.
Radar Mapping
Radar mapping technology uses radio waves to detect and locate objects. It’s particularly useful in applications such as weather monitoring and terrain mapping, where it can provide valuable data regardless of weather conditions.
The versatility of radar mapping makes it a valuable tool in various sectors, from aviation to meteorology.
Application segmentation: transportation, construction, and environmental monitoring
Mapping technology is versatile and has many uses, including transportation, construction, and environmental monitoring. It is now essential in many industries, improving efficiency, precision, and decision-making.
Transportation and Mapping
In the transportation sector, mapping technology plays a crucial role in route optimization and the development of autonomous vehicles. By creating detailed maps of road networks, mapping technology helps in reducing travel times, improving traffic flow, and enhancing safety. For instance, companies like Google and Apple are investing heavily in mapping technology to improve their navigation services.
The application of mapping technology in autonomous vehicles is particularly noteworthy. Autonomous vehicles rely on high-definition maps to navigate through complex environments. These maps provide detailed information about the road geometry, traffic signals, and other critical features that are essential for safe navigation.
Construction and Environmental Monitoring Applications
In construction, mapping technology is used for site planning and monitoring. It helps in creating detailed topographic maps of the construction site, which are used to plan the construction process, monitor progress, and identify potential issues. Technologies like LIDAR and photogrammetry are commonly used in this sector.
Environmental monitoring is another significant application area for mapping technology. It is used to track deforestation, monitor climate changes, and manage natural resources. For example, satellite-based mapping technologies are used to monitor forest cover and detect changes in land use.
| Application Area | Key Technologies | Benefits |
| Transportation | GPS, LIDAR, Autonomous Vehicles | Route Optimization, Improved Safety |
| Construction | LIDAR, Photogrammetry | Site Planning, Progress Monitoring |
| Environmental Monitoring | Satellite Imagery, GIS | Deforestation Tracking, Climate Change Monitoring |
Global trends in real-time mapping and autonomous navigation systems
The global trend towards real-time mapping is transforming the way we navigate and interact with our environment. This shift is driven by the increasing need for accurate and up-to-date spatial data, which is crucial for various applications, including autonomous vehicles and smart city initiatives.
Real-Time Mapping
Real-time mapping enables the creation of dynamic maps that can be updated instantly, reflecting changes in the environment. This capability is essential for autonomous vehicles, which rely on real-time data to navigate safely and efficiently.
Some of the key benefits of real-time mapping include:
- Improved navigation accuracy
- Enhanced decision-making for autonomous systems
- Increased efficiency in various industries, such as construction and transportation
Autonomous Navigation Systems
Autonomous navigation systems rely heavily on real-time mapping to make informed decisions. These systems use a combination of technologies, including LIDAR, GPS, and radar, to navigate through complex environments.
The integration of real-time mapping with autonomous navigation systems is expected to drive significant advancements in the field. For instance, real-time mapping enables autonomous vehicles to detect and respond to changes in their surroundings, such as road closures or new traffic patterns.
The future of autonomous navigation systems looks promising, with ongoing developments in high-definition 3D mapping and AI-powered analytics. These advancements will further enhance the capabilities of autonomous systems, enabling them to navigate even more complex environments.
Some of the key trends to watch in the coming years include:
- The increasing adoption of real-time mapping in various industries
- The development of more sophisticated autonomous navigation systems
- The integration of real-time mapping with other technologies, such as IoT and 5G
U.S. Leadership in Mapping for Autonomous Vehicles and Urban Mobility
The U.S. is leading the way in developing mapping technology for autonomous vehicles, driving innovation in urban mobility. This leadership is fueled by significant investments in research and development, as well as the presence of key players in the mapping technology market.
Mapping for Autonomous Vehicles
The development of mapping technology for autonomous vehicles is a complex task that requires high accuracy and precision. Companies in the U.S. are working on creating detailed maps that can be used by autonomous vehicles to navigate safely and efficiently.
Key technologies
Key technologies being used include LIDAR, GPS, and photogrammetry. These technologies enable the creation of highly accurate maps that are essential for the safe operation of autonomous vehicles.
Urban mobility initiatives
Urban mobility initiatives are also a key area of focus in the U.S. Cities are leveraging mapping technology to improve traffic management and public transportation. For example, cities are using real-time mapping data to optimize traffic signal timing and reduce congestion.
- Improving traffic management
- Enhancing public transportation
- Reducing congestion
By investing in mapping technology, the U.S. is not only advancing the development of autonomous vehicles but also creating more efficient and sustainable urban mobility systems.
South Korea’s investment in smart city technologies and infrastructure mapping
With significant investments in smart city initiatives, South Korea is transforming its urban landscapes through advanced infrastructure mapping. This strategic move is aimed at enhancing the quality of urban living by leveraging technology to create more efficient, sustainable, and livable cities.
Smart City Initiatives
South Korea’s smart city initiatives are comprehensive, encompassing a wide range of technologies and innovations. A key aspect of these initiatives is the use of advanced mapping technologies to gather and analyze data on urban infrastructure. This data is crucial for planning, managing, and maintaining the infrastructure of smart cities.
Infrastructure Mapping in South Korea
Infrastructure mapping in South Korea involves the use of various technologies such as LIDAR, GPS, and photogrammetry to create detailed maps of urban infrastructure. These maps are essential for identifying areas that require maintenance or upgrade, thereby enabling proactive infrastructure management.
- Enhanced urban planning and management
- Improved public services through data-driven decision-making
- Increased efficiency in infrastructure maintenance and development
The U.K.’s regulatory framework on geospatial data and privacy
The U.K.’s approach to regulating geospatial data emphasizes both innovation and privacy protection. This balanced approach is crucial in ensuring that the benefits of geospatial data are realized while protecting individual privacy rights.
Key Components of the Regulatory Framework
The U.K.’s regulatory framework for geospatial data is complex, involving various laws and guidelines. Key legislation includes the Data Protection Act 2018 and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which provide a foundation for data protection and privacy.
Geospatial Data and Privacy Concerns
Geospatial data, which includes information related to the geographical location of features or boundaries, raises significant privacy concerns. The collection and use of such data must be carefully managed to prevent privacy breaches. The U.K.’s regulatory framework addresses these concerns through strict guidelines on data handling and use.
| Regulatory Aspect | Description | Impact on Geospatial Data |
| Data Protection Act 2018 | Provides a legal framework for data protection | Ensures that geospatial data is handled in compliance with data protection laws |
| GDPR | Regulates the processing of personal data | Impacts how geospatial data that includes personal information is processed |
| Geospatial Data Regulations | Specific guidelines for the use of geospatial data | Ensures that geospatial data is used responsibly and with respect for privacy |
The regulatory framework in the U.K. is designed to be flexible, evolving with technological advancements and changing societal needs. This adaptability is crucial in maintaining a balance between innovation and privacy protection.
In summary, the U.K.’s regulatory framework for geospatial data and privacy is comprehensive and designed to protect individual rights while fostering innovation. Understanding this framework is essential for organizations and individuals involved in the collection, storage, and use of geospatial data. This understanding becomes even more critical when considering the responsible use of spatial data, which must align with these regulations while also being mindful of ethical considerations.
Future developments in high-definition 3D mapping and AI-powered analytics
The future of mapping technology is set to be transformed by advancements in high-definition 3D mapping and AI-powered analytics. These technologies are changing how we perceive and engage with our surroundings.
Advancements in Mapping Technology
High-definition 3D mapping enables the creation of highly accurate and detailed models of the environment. This technology has numerous applications, including urban planning, autonomous vehicles, and environmental monitoring.
Key benefits of high-definition 3D mapping include:
- Enhanced accuracy and detail
- Improved decision-making capabilities
- Increased efficiency in various industries
AI-powered analytics can process vast amounts of data to provide insights and predictions. This technology is crucial for industries that rely on complex data analysis, such as autonomous vehicles and smart city initiatives.
The combination of these technologies enables the creation of sophisticated models that can be used to predict and analyze various scenarios, leading to better decision-making.
| Technology | Application | Benefits |
| High-definition 3D Mapping | Urban Planning, Autonomous Vehicles | Enhanced accuracy, Improved decision-making |
| AI-Powered Analytics | Data Analysis, Predictive Modeling | Increased efficiency, Better predictions |
Market competitors in mapping technologies for smart infrastructure
As smart infrastructure continues to evolve, the competition among mapping technology providers is intensifying. The demand for accurate and efficient mapping solutions has attracted numerous players to the market, making it increasingly competitive.
Key Competitors
The market for mapping technologies in smart infrastructure is dominated by several key competitors. These companies are using their technological expertise and innovative capabilities to gain an advantage over others.
Leading Companies
Companies like Google, Apple, and Microsoft are investing heavily in mapping technologies, including LIDAR and photogrammetry.
Specialized Firms
Specialized firms like Trimble and Hexagon are also major players, offering a range of mapping solutions tailored to specific industries.
The competitive landscape is characterized by rapid innovation, strategic partnerships, and a focus on integrating mapping technologies with other emerging technologies like AI and IoT.
- Innovation is a key driver, with companies continually updating their technologies to stay ahead.
- Strategic partnerships are also crucial, enabling companies to expand their offerings and reach new markets.
- Integration with other technologies is enhancing the capabilities of mapping solutions, making them more valuable to customers.
Understanding the competitive dynamics is essential for businesses looking to enter or expand in the mapping technology market for smart infrastructure. Furthermore, exploring the potential of geospatial data could provide additional insights and opportunities in this rapidly evolving field.
Overall
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Global Mapping Technology Report |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Segment by Type |
· LIDAR · GPS · Photogrammetry · Radar mapping technologies |
| Segment by Application |
· Transportation · Construction · Environmental Monitoring |
| Geographies Covered |
· North America (United States, Canada) · Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Russia) · Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan) · Southeast Asia (India) · Latin America (Mexico, Brazil) |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
The mapping technology market is about to undergo a major change, thanks to improvements in LIDAR, GPS, and AI-powered analytics. As the market keeps evolving, it will be essential for stakeholders to understand the trends, challenges, and competitive landscape.
Future Prospects
The future of mapping technology holds much promise, with potential applications across various sectors that can transform industries and improve lives. The integration of real-time mapping and autonomous navigation systems is expected to revolutionize transportation, construction, and environmental monitoring.
As the market outlook suggests, the mapping technology industry is poised for substantial growth, driven by increasing demand for smart city initiatives and infrastructure development. Companies like Google, Apple, and HERE Technologies are at the forefront of this innovation, pushing the boundaries of what is possible with mapping technology.
Global Mapping Technology Market Report (Can Read by Free sample) – Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Mapping Technology Market Analysis Overview
- Competitive Forces Analysis (Porter’s Five Forces)
- Strategic Growth Assessment (Ansoff Matrix)
- Industry Value Chain Insights
- Regional Trends and Key Market Drivers
- Mapping TechnologyMarket Segmentation Overview
Chapter 2: Competitive Landscape
- Global Mapping Technologyplayers and Regional Insights
- Key Players and Market Share Analysis
- Sales Trends of Leading Companies
- Year-on-Year Performance Insights
- Competitive Strategies and Market Positioning
- Key Differentiators and Strategic Moves
Chapter 3: Mapping Technology Market Segmentation Analysis
- Key Data and Visual Insights
- Trends, Growth Rates, and Drivers
- Segment Dynamics and Insights
- Detailed Market Analysis by Segment
Chapter 4: Regional Market Performance
- Consumer Trends by Region
- Historical Data and Growth Forecasts
- Regional Growth Factors
- Economic, Demographic, and Technological Impacts
- Challenges and Opportunities in Key Regions
- Regional Trends and Market Shifts
- Key Cities and High-Demand Areas
Chapter 5: Mapping Technology Emerging and Untapped Markets
- Growth Potential in Secondary Regions
- Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Chapter 6: Product and Application Segmentation
- Product Types and Innovation Trends
- Application-Based Market Insights
Chapter 7: Mapping Technology Consumer Insights
- Demographics and Buying Behaviors
- Target Audience Profiles
Chapter 8: Key Findings and Recommendations
- Summary ofMapping TechnologyMarket Insights
- Actionable Recommendations for Stakeholders
Access the study in MULTIPLEFORMATS
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1-866-739-3133
Email: infor@wkinformation.com
What is driving the growth of the Mapping Technology Market?
The growth of the Mapping Technology Market is driven by increasing demand for accurate and efficient mapping technologies across various industries, including transportation, construction, and environmental monitoring.
What are the key technologies used in mapping?
The key technologies used in mapping include LIDAR, GPS, photogrammetry, and radar mapping. Each technology has its unique applications and advantages.
How is mapping technology used in autonomous vehicles?
Mapping technology is crucial for autonomous vehicles, providing high-definition maps for navigation and decision-making.
What are the challenges facing the Mapping Technology Market?
The Mapping Technology Market faces challenges related to data accuracy, infrastructure costs, and integration issues.
What is the role of AI-powered analytics in mapping technology?
AI-powered analytics is essential for understanding the large volumes of data gathered through mapping technologies. It helps various industries make informed decisions based on this data.
How is mapping technology used in smart city initiatives?
Mapping technology is used in smart city initiatives to enhance public services, improve traffic management, and support urban planning.
Why is high-definition 3D mapping important?
High-definition 3D mapping allows us to create precise and detailed models of our surroundings. This technology is transforming fields like city planning and self-driving cars.
Who are the key competitors in the Mapping Technology Market?
The Mapping Technology Market is competitive, with key players including companies that specialize in LIDAR, GPS, and other mapping technologies.
What is the future of the Mapping Technology Market?
The future of the Mapping Technology Market is set for significant growth, driven by advancements in technologies like LIDAR, GPS, and AI-powered analytics.
How is geospatial data regulated?
Geospatial data is regulated through frameworks that address concerns related to data protection, privacy, and the beneficial use of this data. These regulations often involve comprehensive policies that ensure the responsible use of such sensitive information, as depicted in the image below.

