Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market to Surge Past $16.61 Billion by 2025 Led by US, China, and India
A comprehensive analysis of the solar photovoltaic wafer market dynamics between the US, China, and India, examining trade policies under Trump’s administration, market shifts, manufacturing competition, and future industry projections. The report explores how international trade strategies impact renewable energy objectives, domestic manufacturing capabilities, and global supply chains in these key markets, while considering ethical considerations and investment incentives shaping the industry’s future.
- Last Updated:
Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Forecast for Q1 and Q2 of 2025
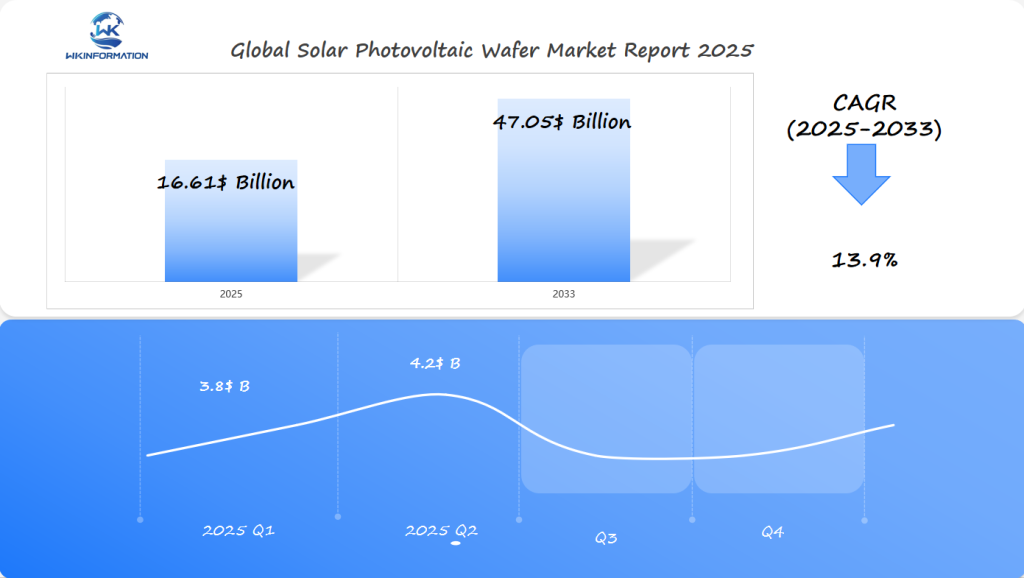
The global Solar Photovoltaic Wafer market is projected to reach USD 16.61 billion in 2025, with a promising CAGR of 13.9% through 2033. The market’s early stages in 2025 are expected to showcase a differentiated growth pattern, with significant contributions from the US, China, and India.
In Q1, the market size is forecast to be approximately USD 3.8 billion, fueled by strong demand in China and India, where the government’s push for renewable energy solutions continues to gain momentum. China, being a major manufacturing hub for photovoltaic wafers, is expected to contribute a large portion of this figure. The US, on the other hand, is anticipated to experience a moderate uptick in demand due to ongoing advancements in solar energy technology and infrastructure.
By Q2, the market is expected to reach around USD 4.2 billion, reflecting an increase in production capacities and installation rates across the three leading countries. While the US may show steady growth, China and India are likely to see more pronounced increases, driven by large-scale solar power projects and ambitious renewable energy targets. Given these factors, the US, China, and India stand out as the most critical regions to watch in the first half of 2025.
Analyzing the Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market: Upstream and Downstream Dynamics
The solar photovoltaic wafer market is closely connected to its supply chain, which consists of two main segments: upstream and downstream.
Upstream Segment: Raw Material Extraction and Processing
The upstream segment involves the extraction and processing of raw materials, with polysilicon being a crucial component. Polysilicon, derived from silicon, serves as the foundational element for wafer manufacturing. To achieve the high-purity levels required for solar applications, polysilicon undergoes purification processes. The availability and cost of this material can significantly impact wafer production costs, making it a critical factor in the industry’s supply chain dynamics.
In the upstream stage, the manufacturing process involves several steps:
- Purification of Silicon: Raw silicon is purified to produce polysilicon.
- Ingot Formation: Polysilicon is melted and crystallized into ingots.
- Wafer Slicing: Ingots are sliced into thin wafers suitable for solar cell production.
Downstream Segment: Distribution and Installation Activities
The downstream segment encompasses activities related to distribution and installation, which are crucial for transforming manufactured wafers into functional solar panels. This phase includes:
- Distribution: Transporting wafers to module manufacturers who assemble them into solar panels.
- Installation: Deploying these panels in residential, commercial, or utility-scale projects.
The value chain in this industry extends beyond mere production, with distribution and installation playing vital roles in bringing solar power solutions to end-users. Efficient distribution networks ensure timely delivery of wafers, while skilled installation teams maximize panel performance through precise mounting techniques.
Understanding the Interconnected Stages
Understanding both upstream and downstream activities offers insight into the complexities of the solar photovoltaic wafer market. These interconnected stages illustrate how raw material availability, manufacturing efficiency, and effective distribution channels collectively contribute to meeting global renewable energy demands. As the market evolves, innovations within each segment are expected to drive further growth and sustainability in the coming years.
Breakthrough Trends Shaping the Future of Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Industry
Technological Advancements in Solar Wafer Technology
Key innovations are at the heart of the solar photovoltaic wafer industry’s growth. Advances in efficiency and durability have transformed how wafers contribute to renewable energy solutions. The development of perovskite solar cells is a notable example, offering a potential increase in efficiency while reducing production costs. These cells are lightweight and flexible, providing diverse application possibilities.
Impact of Digitalization on Production
Digitalization plays a crucial role in enhancing production efficiency and reducing costs. By integrating automated manufacturing processes and real-time data analytics, companies can optimize wafer production, minimize waste, and improve quality control. Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical systems—are also being utilized to simulate and refine manufacturing processes before actual implementation.
Emerging Market Trends
Consumer demand for solar wafers is increasingly influenced by sustainability considerations and aesthetic appeal:
- Sustainability: Consumers are becoming more environmentally conscious, driving demand for solar solutions with a lower carbon footprint. Manufacturers are responding with eco-friendly practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing waste.
- Aesthetic Appeal: As solar technology becomes more integrated into everyday life, aesthetics gain importance. Innovations like transparent solar panels enable integration into windows and facades without compromising building design.
The convergence of these trends underscores the dynamic nature of the solar photovoltaic wafer industry. As technological advancements continue to unfold, they promise not only to meet growing energy demands but also to align with evolving consumer expectations. This landscape offers exciting opportunities for growth and innovation in the coming years.
Barriers and Constraints Slowing Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Growth
The growth of the solar photovoltaic wafer market is facing several obstacles that could slow it down. One of the biggest challenges is trade restrictions, which have a significant impact on market expansion. Countries impose tariffs and non-tariff measures that can affect the cost and distribution of solar wafers across international markets. For example, when tariffs are imposed on imported solar components, it can lead to higher costs for domestic manufacturers and potentially slow down adoption rates.
Another critical challenge is the dependence on fossil fuels for certain manufacturing processes within the industry. While solar energy itself is clean and renewable, the production of solar wafers often relies on energy generated from fossil fuels. This creates a contradiction where the industry’s sustainability goals are undermined by its own production practices. Transitioning to greener energy sources for manufacturing could help align production processes with the environmental benefits of solar energy.
Economic challenges also play a role in restraining market growth. The fluctuation in raw material prices poses a risk to manufacturers who depend on stable supply chains and cost structures to maintain competitive pricing. Polysilicon, a crucial raw material for wafer production, is subject to price volatility that can affect overall manufacturing costs. Additionally, access to financing remains limited for many projects, particularly in emerging markets where investment in renewable infrastructure is still developing.
These barriers highlight the complexities facing the solar photovoltaic wafer market as it attempts to scale up and meet increasing global demand. Addressing these issues requires coordinated efforts among industry stakeholders, policymakers, and financial institutions to ensure that the path towards sustainable energy solutions is both viable and economically feasible.

Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Geopolitical Analysis Global Trade and Policy Impacts
The solar photovoltaic wafer market is heavily influenced by geopolitical factors, with international trade policies playing a crucial role in shaping trade patterns. Countries such as the United States, China, and India are at the forefront, each with unique strategies and challenges.
Influence of Global Politics on Trade Patterns
- China dominates the global solar supply chain, controlling over 80% of the manufacturing stages. This dominance stems from substantial investments exceeding $50 billion in photovoltaic supply capacity.
- The United States is focusing on expanding its domestic production capabilities to decrease reliance on imports, particularly from China.
- India aims to bolster its manufacturing infrastructure for solar wafers and ingots, aligning with national energy goals to reduce import dependency.
Tariffs and Sanctions Impacting Supply Chains
Trade barriers such as tariffs and sanctions significantly impact the solar wafer market:
- The U.S. has imposed tariffs on Chinese solar products, affecting cost structures and supply chain dynamics.
- Non-tariff measures also play a role, including quotas and stringent quality standards that manufacturers must meet to enter certain markets.
These trade policies can lead to increased production costs and influence the strategic decisions of manufacturers globally.
Role of Government Policies
Governments worldwide are implementing policies to promote renewable energy adoption:
- In China, supportive government initiatives have propelled it to become a leader in solar PV equipment manufacturing.
- The U.S. government offers incentives for clean energy projects, fostering a conducive environment for domestic manufacturers.
- India’s “Make in India” initiative emphasizes enhancing local manufacturing capabilities, supporting the growth of its solar sector.
Government regulations not only encourage renewable energy adoption but also create opportunities for innovation and investment in domestic markets. These policies are pivotal in steering the market towards sustainable growth while addressing international trade challenges.
Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Segmentation by Type: Key Wafer Technologies
The solar photovoltaic wafer market offers a variety of wafer types, each with distinct characteristics that cater to different applications and preferences. Monocrystalline wafers, known for their high efficiency and longevity, are crafted from a single crystal structure. This uniformity allows them to convert sunlight into electricity more effectively than other types. However, their production process is more complex and costly, which can impact their cost-effectiveness.
In contrast, polycrystalline wafers are made from multiple silicon crystals melted together. While they typically have lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline counterparts, they offer a more affordable solution for budget-conscious projects. Their simpler manufacturing process reduces costs, making them an attractive option for large-scale installations where budget constraints are significant.
Thin-film technology represents an alternative approach by using layers of photovoltaic material on surfaces like glass or metal. Thin-film wafers stand out due to their flexibility and lightweight nature, which makes them suitable for unconventional applications such as building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) or portable solar solutions. However, thin-film technologies generally lag behind in efficiency compared to crystalline silicon wafers.
Each type brings its own set of advantages and disadvantages:
- Monocrystalline Wafers:Advantages: High efficiency, long lifespan
- Disadvantages: Higher production costs
- Polycrystalline Wafers:Advantages: Cost-effective, simpler manufacturing process
- Disadvantages: Lower efficiency
- Thin-Film Technology:Advantages: Flexible, lightweight
- Disadvantages: Lower efficiency
Understanding these differences helps stakeholders make informed decisions about which technology best suits their specific needs and budgetary constraints. The choice of wafer type directly influences the overall performance and cost-efficiency of solar power installations.
Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Segmentation by Application Core Industry Uses
The solar photovoltaic wafer market finds its applications spanning across various sectors, each with unique requirements and benefits. Understanding these applications helps in appreciating the versatility and potential of solar wafers in addressing global energy needs.
Residential Applications
In residential settings, solar wafers play a crucial role in providing clean and sustainable energy solutions. Homeowners use the efficiency of these wafers to power household appliances, heating systems, and lighting. The compact size of monocrystalline and polycrystalline wafers makes them ideal for rooftop installations, offering significant energy savings and reducing reliance on traditional electricity grids.
Commercial Applications
For commercial entities, solar wafers are essential for reducing operational costs and enhancing sustainability credentials. Businesses in sectors such as retail, hospitality, and manufacturing utilize solar panels incorporating these wafers to offset electricity expenses. The long-term cost-effectiveness combined with governmental incentives for renewable adoption enhances their appeal for commercial use.
Utility-Scale Projects
Utility-scale projects represent the largest segment of the solar photovoltaic wafer market. These large installations often span several acres and can power thousands of homes or businesses. Solar farms utilizing high-efficiency wafers contribute significantly to the grid’s renewable energy supply. They are essential in meeting renewable energy targets set by governments worldwide.
Specific Use Cases
- Agricultural Sector: Solar wafers are increasingly used in agriculture for water pumping systems, greenhouse heating, and powering equipment.
- Telecommunications: Off-grid telecommunications towers benefit from solar wafer technology to ensure uninterrupted service.
- Remote Areas: In regions lacking reliable electricity infrastructure, solar wafers provide a sustainable solution for electrification.
These diverse applications underscore the significance of solar wafers in advancing global energy solutions. Their adaptability across different sectors demonstrates their vital role in propelling the transition towards renewable energy sources.
Global Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Expansion Across Regions Opportunities for Growth
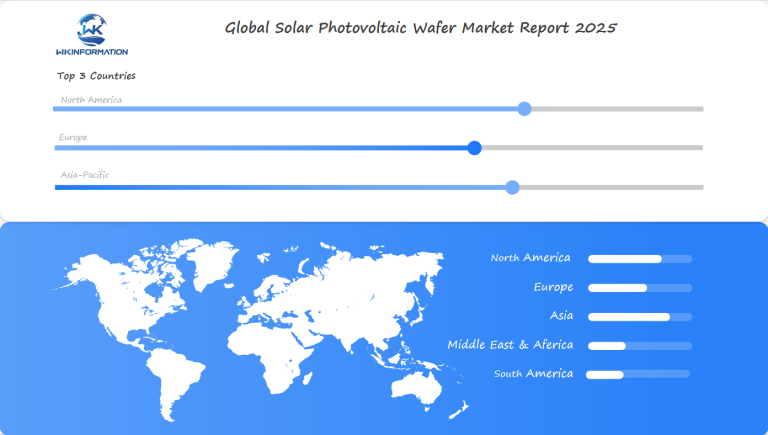
The global solar photovoltaic wafer market is witnessing significant expansion across various regions, each contributing uniquely to the industry’s evolution. Regional analysis reveals distinct dynamics in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, with key growth markets emerging in the US, China, and India.
North America
United States
The US solar wafer market is on a promising trajectory. With extensive support from government policies and incentives aimed at increasing renewable energy adoption, the demand for solar wafers is on the rise. Investments in domestic manufacturing capabilities are also bolstering the market’s growth prospects.
Europe
Regulatory Frameworks
Europe’s focus on sustainability and stringent regulatory frameworks drives the demand for renewable energy solutions. Countries such as Germany and Spain have pioneered solar energy adoption, creating robust opportunities for wafer manufacturers.
Asia-Pacific
China
As the dominant force in the solar photovoltaic supply chain, China continues to lead the market. With its control over 80% of manufacturing stages, China’s investment in photovoltaic supply capacity remains unparalleled.
India
Rapid advancements in solar technology and aggressive governmental targets for renewable energy are propelling India’s market forward. The country’s initiatives to enhance domestic manufacturing capabilities aim to reduce reliance on imports and foster local industry growth.
Regional Variations in Demand Drivers
The pace of expansion varies significantly across these regions due to differing demand drivers:
- Economic Incentives: Subsidies and tax incentives play a crucial role in shaping market dynamics.
- Energy Policies: National energy policies focusing on reducing carbon emissions bolster renewable energy sources like solar wafers.
Regulatory Frameworks
Regulatory environments influence the market’s growth rate by either facilitating or constraining industry activities. While some countries offer generous subsidies and support for clean energy projects, others impose trade barriers that affect international collaborations.
This regional diversity highlights not only the current opportunities but also underscores potential challenges that must be navigated to ensure successful market penetration and expansion worldwide.
US Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Analysis Unveiling Growth Potential
The United States is becoming an important player in the solar photovoltaic wafer market, with its growth showing great potential. Several factors contribute to this positive trend:
1. Increased Demand for Renewable Energy
The US is seeing a strong push towards renewable energy sources, driven by both government and consumer demand for sustainable energy solutions. This shift creates a need for solar wafers, which are essential for producing solar panels.
2. Government Initiatives and Policies
Federal and state-level policies are actively supporting the solar industry. Incentives like tax credits and subsidies encourage the use of solar technology, leading to more adoption of solar wafers.
3. Technological Advancements
The US benefits from advanced research in solar technologies. Innovations in wafer design and production processes improve efficiency and lower costs, making solar energy more accessible and appealing.
4. Domestic Manufacturing Growth
There is a concerted effort to strengthen domestic manufacturing capabilities to reduce dependence on imports, especially from China. Investing in manufacturing infrastructure creates local jobs and makes the supply chain more resilient.
5. Strategic Collaborations
Partnerships between government bodies, private companies, and research institutions create an environment that encourages innovation and growth in the sector.
These factors together suggest a bright future for the US solar photovoltaic wafer market, with opportunities for growth and development.
China Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Analysis Exploring Key Trends
China is a major player in the solar photovoltaic wafer market, with significant control over global supply chains. The country produces over 80% of the manufacturing stages for solar panels, including wafer production. This leadership is a result of investments exceeding $50 billion in photovoltaic supply capacity, which have created more than 300,000 manufacturing jobs since 2011.
Several key factors are driving China’s market growth:
1. Technological Advancements
Chinese manufacturers are leading the way in innovation, improving wafer efficiency and durability. These advancements are essential for staying competitive and meeting increasing global demand.
2. Government Support
Strategic government policies continue to support renewable energy initiatives, providing subsidies and incentives that promote domestic production and reduce reliance on imports.
3. Sustainability Focus
As sustainability becomes a critical concern worldwide, China’s emphasis on environmental responsibility is appealing to both domestic and international markets. Efforts to minimize carbon footprints in production processes align with global sustainability goals.
China’s significant role in polysilicon production further strengthens its position in the market. With major manufacturers located within its borders, China not only influences pricing but also establishes industry standards that shape global practices.
India Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Analysis Mapping Future Opportunities
India is a growing market for solar photovoltaic wafers, driven by its ambitious renewable energy goals and high demand for clean energy solutions. The country aims to have 280 GW of installed solar capacity by 2030, making it a key player in the global adoption of solar energy.
Key Growth Drivers in India:
- Government Initiatives: Policies like the “National Solar Mission” aim to increase domestic manufacturing capabilities, reducing dependence on imports and fostering local innovation.
- Investment in Technology: India is increasingly investing in advanced wafer technologies to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. This strategic focus is crucial for meeting both domestic and international energy needs.
- Private Sector Involvement: Collaboration between public initiatives and private companies speeds up technological advancements, with businesses exploring partnerships to increase production capacities.
Emerging Opportunities:
- Domestic Manufacturing: Efforts to boost local production of wafers and cells align with India’s broader energy security goals.
- Innovation Hubs: Establishing centers for research and development can drive breakthroughs in wafer technology, enhancing competitiveness on the global stage.
- Export Potential: As India’s production capacity grows, so too does its potential to become a significant exporter within the global solar PV supply chain.
India’s dynamic market environment shows its potential to make a significant contribution to the growth of the global solar PV sector.
Future of Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Innovations Shaping the Industry
Technological advancements are crucial in transforming the solar photovoltaic wafer market. Key innovations include:
1. High-Efficiency Wafer Technologies
The shift towards PERC (Passivated Emitter Rear Cell) and bifacial technology is enhancing efficiency. These technologies allow for greater light capture, boosting overall energy output.
2. Durability Improvements
Research into materials such as silicon carbide and graphene holds the promise of making wafers more resilient to environmental stressors, potentially extending their lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
3. Smart Manufacturing
Digitalization in manufacturing processes is leading to significant cost reductions. Automation and AI-driven analytics streamline production, cutting down on waste and increasing throughput.
4. Sustainable Practices
There is a growing focus on sustainability, with manufacturers exploring eco-friendly materials and recycling methods to minimize environmental impact.
5. Aesthetic Designs
As demand grows for building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), there’s an increased emphasis on aesthetically pleasing designs that blend easily with modern architecture.
These innovations not only enhance performance but also address consumer preferences and regulatory demands. The industry stands at the brink of a transformation, driven by these technological leaps, setting the stage for sustained growth and broader adoption of solar energy solutions globally.
Competitive Landscape: Who’s Dominating the Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market
The solar photovoltaic wafer market is a dynamic arena, with several key players driving its growth and innovation.
-
Jinko Solar Holding Co., Ltd.
-
GCL-Poly Energy Holdings Limited
-
LONGi Green Energy Technology Co Ltd
-
CETC Solar Energy Holdings Co
-
Sino-American Silicon Products Inc.
-
Lanco Solar
-
Renewable Energy Corporation
-
Zhonghuan Semiconductor Corporation
-
Nexolon Co., Ltd.
-
Green Energy Technology
Overall
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Global Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Report |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Segment by Type |
· Monocrystalline Wafers · Polycrystalline Wafers · Thin-Film Technology |
| Segment by Application |
· Residential Applications · Commercial Applications · Utility-Scale Projects · Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) · Others |
| Geographies Covered |
· North America (United States, Canada) · Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Russia) · Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan) · Southeast Asia (India) · Latin America (Mexico, Brazil) |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
The solar photovoltaic wafer market is expected to grow significantly due to the increasing global demand for renewable energy sources and major technological advancements. It is projected that the market could exceed $16.61 billion by 2025, with countries such as the US, China, and India leading this growth. These countries are not only at the forefront of solar energy adoption but are also strengthening their manufacturing capabilities, which will be crucial in shaping the industry’s future.
Key trends like digitalization and improved production efficiency are lowering costs and enhancing the durability of solar wafers. These innovations are vital in meeting the rising demand for sustainable energy solutions. However, challenges still remain, such as trade barriers and dependence on fossil fuels during manufacturing processes.
Government policies promoting renewable energy adoption are driving market growth and creating a favorable environment for domestic manufacturers. The competitive landscape is constantly evolving, with major players striving to innovate and capture larger market shares.
Although there are obstacles, the combination of technological advancements and strategic government support indicates a positive outlook for the solar photovoltaic wafer market. The ongoing commitment to sustainability and innovation is likely to push this sector forward in the coming years, presenting numerous opportunities for investment and development.
Global Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Report (Can Read by Free sample) – Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Analysis Overview
- Competitive Forces Analysis (Porter’s Five Forces)
- Strategic Growth Assessment (Ansoff Matrix)
- Industry Value Chain Insights
- Regional Trends and Key Market Drivers
- Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Segmentation Overview
Chapter 2: Competitive Landscape
- Global Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Players and Regional Insights
- Key Players and Market Share Analysis
- Sales Trends of Leading Companies
- Year-on-Year Performance Insights
- Competitive Strategies and Market Positioning
- Key Differentiators and Strategic Moves
Chapter 3: Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Segmentation Analysis
- Key Data and Visual Insights
- Trends, Growth Rates, and Drivers
- Segment Dynamics and Insights
- Detailed Market Analysis by Segment
Chapter 4: Regional Market Performance
- Consumer Trends by Region
- Historical Data and Growth Forecasts
- Regional Growth Factors
- Economic, Demographic, and Technological Impacts
- Challenges and Opportunities in Key Regions
- Regional Trends and Market Shifts
- Key Cities and High-Demand Areas
Chapter 5: Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Emerging and Untapped Markets
- Growth Potential in Secondary Regions
- Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Chapter 6: Product and Application Segmentation
- Product Types and Innovation Trends
- Application-Based Market Insights
Chapter 7: Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Consumer Insights
- Demographics and Buying Behaviors
- Target Audience Profiles
Chapter 8: Key Findings and Recommendations
- Summary of Solar Photovoltaic Wafer Market Insights
- Actionable Recommendations for Stakeholders
Access the study in MULTIPLEFORMATS
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1-866-739-3133
Email: infor@wkinformation.com
What is the projected growth of the solar photovoltaic wafer market by 2025?
The solar photovoltaic wafer market is projected to grow to $16.61 billion by 2025, highlighting its increasing importance in renewable energy generation.
What are the key upstream materials involved in solar wafer production?
The upstream supply chain for solar wafer production primarily involves raw materials such as polysilicon, which plays a crucial role in the manufacturing of solar wafers.
What technological advancements are shaping the future of the solar photovoltaic wafer industry?
Key innovations driving market growth include improvements in efficiency and durability of solar wafers, along with the impact of digitalization on production efficiency and cost reduction.
What barriers are currently slowing down the growth of the solar photovoltaic wafer market?
Barriers affecting growth include trade restrictions, dependence on fossil fuels for certain manufacturing processes, and economic challenges like fluctuating raw material prices.
How do geopolitical factors influence the solar photovoltaic wafer market?
Geopolitical factors significantly impact trade patterns in the solar wafer market, particularly through international trade policies, tariffs, and government regulations that affect supply


