Smart Sensor Market Outlook: $67.16 Billion Global Surge by 2025 with Key Insights from the U.S., Germany, and Japan
Explore the comprehensive analysis of the global smart sensor market, projected to reach $67.16 billion by 2025. This meta description covers supply chain dynamics, technological innovations, market challenges, regional insights from the U.S., Germany, and Japan, and future trends shaping the industry’s growth trajectory.
- Last Updated:
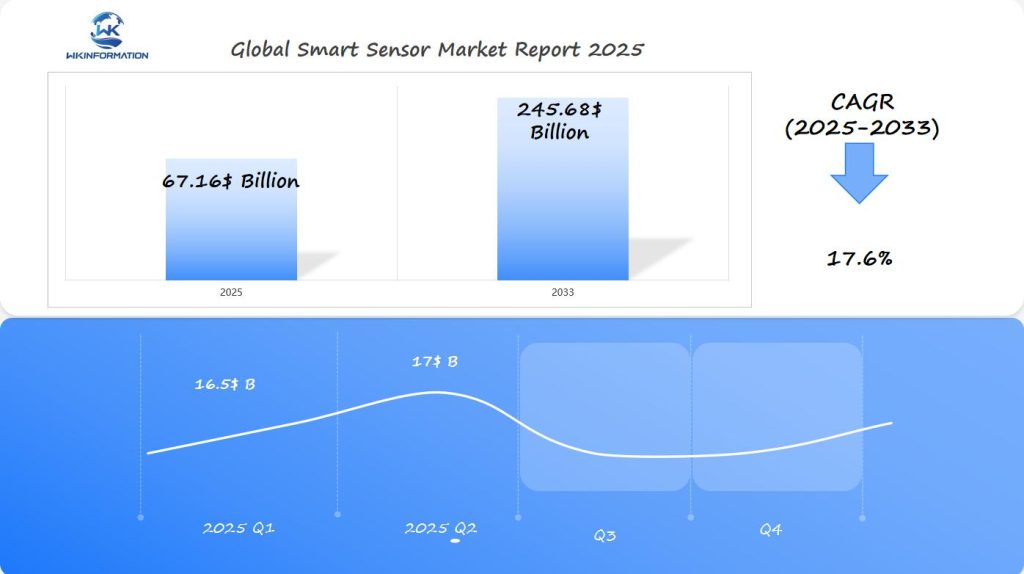
Smart Sensor Market Q1 and Q2 2025 Forecast
The Smart Sensor market is projected to reach $67.16 billion in 2025, with an impressive CAGR of 17.6% from 2025 to 2033. In Q1 2025, the market is expected to generate $16.5 billion, driven by the rapid adoption of IoT-enabled smart sensors in sectors like automotive, healthcare, manufacturing, and home automation. The U.S., Germany, and Japan are leading the market in terms of technology innovation and deployment of smart sensors.
By Q2 2025, the market is expected to grow to $17 billion, with applications in smart homes, smart cities, wearable technology, and automated industrial processes continuing to drive growth. Japan and Germany will lead in industrial automation, while the U.S. will continue to dominate in automotive and healthcare sectors, where advanced sensors are used for driver assistance systems, health monitoring, and precision manufacturing.
Exploring the Upstream and Downstream Dynamics of Smart Sensors
The smart sensor supply chain is a complex network of interconnected parts and processes. It consists of two main levels: upstream and downstream.
Upstream Dynamics: The Role of Raw Material Suppliers
At the upstream level, raw material suppliers play a crucial role in providing essential components to manufacturers. These suppliers provide materials such as silicon wafers, precious metals, and semiconductor materials to component manufacturers.
Key Factors Influencing the Upstream Segment
Several factors can impact the upstream segment of the smart sensor supply chain:
- Raw material availability and pricing fluctuations: The availability and cost of raw materials directly affect the production capabilities of component manufacturers.
- Semiconductor manufacturing capacity: The capacity of semiconductor manufacturers to produce chips can influence the overall supply of smart sensors.
- Research and development investments: Investments in R&D can lead to technological advancements that improve manufacturing processes or create new types of sensors.
- Technological advancement capabilities: The ability of manufacturers to adopt new technologies can impact their competitiveness in the market.
Downstream Dynamics: From Assembly to End-User Applications
The downstream segment includes various activities involved in bringing smart sensors to market. This includes sensor assembly, distribution, and integration into end-user applications.
Industries Benefiting from Smart Sensor Integration
Smart sensors find applications in multiple industries, including:
- Automotive
- Healthcare
- Consumer electronics
Manufacturers in these sectors rely on smart sensors for enhanced functionality, data collection, and automation.
Market Impact of Supply Chain Dynamics
The dynamics within the supply chain have a direct impact on the market for smart sensors. Here are some ways in which these dynamics can influence pricing and availability:
- Raw material shortages drive price increases: If there are shortages in key raw materials like silicon wafers, it can lead to higher costs for sensor manufacturers who rely on those materials.
- Manufacturing bottlenecks create delivery delays: Any disruptions or inefficiencies in the manufacturing process can result in delays in delivering finished products to customers.
- Regional production capabilities influence market accessibility: The production capabilities of different regions can affect how easily certain markets can access smart sensors.
- Supply-demand imbalances affect availability: If there is an imbalance between supply and demand for smart sensors, it can lead to shortages or excess inventory.
Supply Chain Resilience Measures
To mitigate risks associated with these dynamics, stakeholders in the smart sensor supply chain are implementing various resilience measures:
- Diversification of supplier networks: By sourcing raw materials from multiple suppliers instead of relying on a single source, manufacturers can reduce their vulnerability to disruptions.
- Strategic stockpiling of critical components: Maintaining inventory levels of essential components like semiconductors can help manufacturers navigate temporary shortages.
- Investment in local manufacturing capabilities: Building production facilities closer to key markets can minimize transportation costs and improve responsiveness.
- Development of alternative materials and technologies: Exploring substitutes for traditional materials or investing in innovative technologies can provide flexibility in sourcing options.
These efforts aim to create a more robust supply chain that can withstand shocks and ensure a steady flow of smart sensors into various industries.
Technological Trends and Innovations Driving the Smart Sensor Market
IoT Integration: Empowering Smart Sensors
The integration of IoT capabilities has transformed the functionality of smart sensors, allowing them to collect and analyze data in real-time across connected devices. Smart sensors now play a vital role in IoT networks, offering:
- Enhanced Communication Protocols – Supporting multiple wireless standards like Bluetooth LE and Zigbee
- Remote Monitoring Capabilities – Allowing instant access to sensor data from anywhere
- Automated Response Systems – Triggering immediate actions based on collected data
AI and Machine Learning: Unlocking New Possibilities
AI and machine learning algorithms have revolutionized smart sensor applications by enabling:
- Predictive Maintenance – Detecting potential equipment failures before they happen
- Pattern Recognition – Identifying complex relationships and anomalies in data
- Adaptive Learning – Improving accuracy and performance over time
MEMS and CMOS Technologies: Miniaturizing Sensors
MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) and CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) technologies are crucial advancements in making sensors smaller:
Benefits of MEMS Technology:
- Reduced power consumption
- Increased sensitivity
- Smaller sizes
- Enhanced durability
Advantages of CMOS Integration:
- Lower production costs
- Improved signal processing
- Better resistance to noise
- Simpler manufacturing processes
These technological breakthroughs have allowed smart sensors to achieve unmatched levels of accuracy and dependability while still being cost-effective. The combination of IoT connectivity, AI capabilities, and advanced manufacturing methods continues to expand the possibilities of what smart sensors can do in various industries.
Barriers and Challenges Affecting Smart Sensor Growth
The Smart Sensor Market faces significant hurdles that impact its widespread adoption across industries.
High Installation Costs
High installation costs present a substantial barrier, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises. The initial investment includes:
- Hardware procurement costs
- Integration expenses
- Training requirements
- System customization fees
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance creates complex challenges for manufacturers and implementers. Different regions maintain varying standards for:
- Data privacy regulations
- Safety certifications
- Environmental impact assessments
- Industry-specific requirements
Data Security Vulnerabilities
Data Security Vulnerabilities pose critical concerns:
- Unauthorized access risks
- Data manipulation threats
- Network security breaches
- Privacy protection issues
Legacy System Compatibility
Legacy system compatibility remains a persistent challenge. Organizations struggle with:
- Integration of new sensors with existing infrastructure
- Software compatibility issues
- Protocol mismatches
- Performance optimization
Technical Limitations
The market also grapples with technical limitations such as:
- Power consumption constraints
- Signal interference issues
- Calibration requirements
- Maintenance complexities
These challenges directly influence market growth rates and adoption patterns across various sectors. Companies must balance the benefits of smart sensor implementation against these significant barriers while developing strategic solutions to address these limitations.
Geopolitical Factors Impacting Smart Sensor Production and Trade
Global smart sensor production is significantly disrupted by geopolitical tensions. Trade disputes between major economies directly affect manufacturing capabilities and supply chain dynamics.
Key Manufacturing Regions:
- China: Primary producer of sensor components
- Taiwan: Specialized in semiconductor manufacturing
- South Korea: Advanced sensor technology development
- United States: High-end sensor innovation
- Germany: Precision engineering hub
Trade Policy Impact:
- Tariffs on electronic components
- Export restrictions on sensitive technologies
- Intellectual property protection measures
- Regional manufacturing quotas
The semiconductor shortage has intensified competition between nations for smart sensor production capacity. Countries implement strategic policies to protect domestic manufacturing capabilities, leading to shifts in global supply chains.
Regional Manufacturing Strategies:
- Reshoring initiatives
- Local content requirements
- Investment in domestic production facilities
- Strategic partnerships between nations
Supply chain diversification emerges as a critical response to geopolitical uncertainties. Companies establish multiple manufacturing locations across different regions to mitigate risks and ensure continuous production capabilities.
Current Trade Dynamics:
- Rising costs from trade barriers
- Extended lead times
- Increased focus on regional self-sufficiency
- Development of alternative supply routes
These geopolitical factors create a complex landscape where manufacturers must balance cost efficiency with supply chain resilience. The push for technological sovereignty drives investment in local production capabilities, reshaping global smart sensor manufacturing patterns.
Smart Sensor Market Segmentation: Types and Applications
The smart sensor market divides into distinct categories based on sensor types and their applications across industries. Each type serves specific functions and meets unique market demands.
Primary Smart Sensor Types:
- Touch Sensors: Capacitive and resistive variants for user interfaces
- Flow Sensors: Measuring liquid and gas movement in industrial processes
- Temperature Sensors: Monitoring thermal conditions in manufacturing
- Motion Sensors: Detecting movement for security systems
- Pressure Sensors: Tracking pressure changes in automotive systems
Key Application Sectors:
Healthcare
- Patient monitoring devices
- Medical imaging equipment
- Drug delivery systems
- Diagnostic tools
Automotive
- Advanced driver assistance systems
- Engine management
- Tire pressure monitoring
- Safety features
Industrial
- Process automation
- Quality control
- Predictive maintenance
- Asset tracking
Consumer Electronics
- Smartphones
- Wearable devices
- Smart home appliances
- Gaming systems
The market segmentation reflects the growing demand for specialized sensing solutions across these sectors. Each application area drives specific innovations in sensor technology, pushing manufacturers to develop more sophisticated and precise sensing capabilities. The healthcare sector particularly demonstrates rapid adoption, implementing smart sensors in critical patient care and monitoring systems.
How Applications Are Shaping the Smart Sensor Market
Industrial automation is a major force reshaping the smart sensor landscape. Manufacturing facilities implement these sensors for:
- Real-time equipment monitoring
- Predictive maintenance scheduling
- Production line optimization
- Quality control automation
The integration of smart sensors in industrial settings has led to a 25% reduction in maintenance costs and a 20% increase in production efficiency.
Consumer electronics applications drive significant market evolution through:
- Smartphone gesture recognition
- Wearable health monitoring
- Smart home device integration
- Gaming and virtual reality experiences
Environmental monitoring represents another transformative application area:
- Air Quality Management: Smart sensors track pollutants and particulate matter
- Water Conservation: Advanced flow sensors detect leaks and monitor usage
- Agricultural Solutions: Soil moisture and nutrient level monitoring
- Weather Prediction: Enhanced atmospheric data collection
The automotive sector demonstrates rapid sensor adoption rates:
- Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS)
- Battery management in electric vehicles
- Tire pressure monitoring
- Engine performance optimization
These applications continue to push technological boundaries, demanding increased sensor accuracy, reduced power consumption, and enhanced durability. Manufacturing companies report a 30% improvement in operational efficiency through smart sensor implementation.
Regional Insights into the Smart Sensor Market’s Growth
North America: The Leader in Smart Sensor Market
North America is the largest market for smart sensors, accounting for 34% of the revenue in 2024. The region’s success can be attributed to several factors:
- Early adoption of IoT technologies
- Strong presence of tech giants and startups
- Robust industrial automation infrastructure
- High investment in R&D activities
Europe: A Diverse Market with Specific Growth Drivers
The European market has its own unique growth drivers:
- Germany’s manufacturing excellence
- UK’s focus on smart city initiatives
- France’s automotive sector integration
- Nordic countries’ environmental monitoring applications
Asia-Pacific: The Fastest Growing Region
Asia-Pacific is expected to grow the fastest due to:
- China’s massive manufacturing capabilities
- South Korea’s semiconductor expertise
- Taiwan’s specialized sensor production
- India’s emerging automotive and healthcare sectors
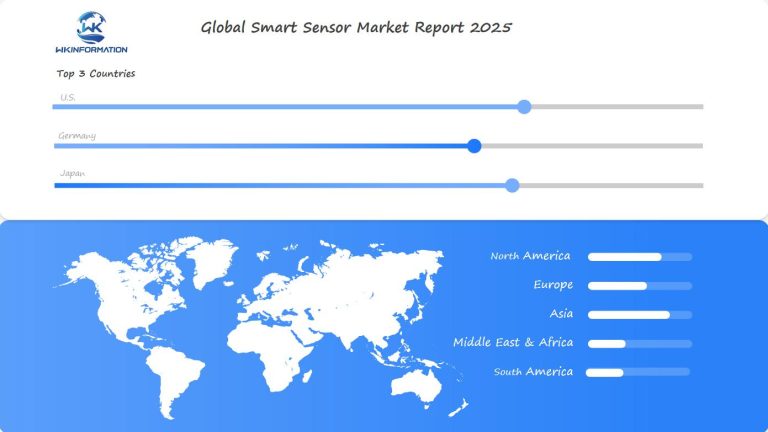
U.S. Market: Leading Innovations in Smart Sensors
The U.S. leads the world in smart sensor innovation with groundbreaking advancements in making devices smaller and more sensitive. American companies have been at the forefront of developing advanced sensor fusion technologies, which combine data from multiple sensors to achieve greater precision and dependability.
Key Innovations from U.S. Laboratories
Some of the most important innovations coming out of U.S. research facilities include:
- Quantum-based sensors – using principles of quantum mechanics for extremely accurate measurements
- Bio-integrated sensors – flexible devices that can seamlessly connect with biological systems
- Self-powered sensors – devices that generate their own energy from the surrounding environment for independent operation
Honeywell’s Contributions to Smart Sensor Development
Honeywell is leading the way in smart sensor development in the United States, introducing:
- Advanced gas detection systems that can predict maintenance needs
- Industrial process sensors with built-in diagnostic capabilities
- Aerospace-grade sensors with improved reliability standards
Factors Driving Growth in the U.S. Market
Several strategic initiatives are contributing to the growth of the smart sensor market in the United States:
- Public-private partnerships that support research on sensors
- Investment in specialized manufacturing facilities
- Collaborations between different industries that speed up technology adoption
The Role of the U.S. Department of Defense
The U.S. Department of Defense plays a crucial role by investing in next-generation sensor technologies, particularly in areas such as:
- Systems for battlefield awareness
- Navigation for autonomous vehicles
- Capabilities for detecting threats
Contributions from American Universities
American universities also make significant contributions through research programs focused on miniaturizing sensors and improving their power efficiency. These institutions work closely with industry partners to bring new technologies into commercial use.
Germany’s Role in Smart Sensor Technology and Demand
Germany is a leader in Europe’s smart sensor industry, thanks to its strong manufacturing sector and dedication to Industry 4.0 initiatives. The country’s market advantage comes from its solid industrial foundation and technological know-how, especially in the automotive and industrial automation fields.
Key Research Initiatives
Germany’s research efforts in smart sensor technology are supported by various initiatives, including:
- The Fraunhofer Institute’s dedicated sensor development programs
- Collaborative projects between universities and industry leaders
- Government-funded research in miniaturization technologies
Leading Companies and Breakthrough Developments
German companies such as Infineon Technologies and Bosch Sensortec are at the forefront of innovation, making significant advancements in:
- MEMS sensor technology
- Smart pressure sensors
- Advanced temperature monitoring systems
Thriving R&D Landscape
The research and development ecosystem in Germany flourishes due to:
- Strategic partnerships between academic institutions and the private sector
- Investment in specialized research facilities
- Emphasis on precision engineering and quality control
Specialized Sensor Applications
Germany’s manufacturing expertise translates into specific sensor applications that require high levels of accuracy and reliability:
- High-precision automotive sensors
- Industrial process monitoring devices
- Environmental sensing solutions
Market Demand and Opportunities
The German smart sensor market benefits from:
- Strong domestic demand from manufacturing sectors
- Export opportunities to global markets
- Integration with existing industrial infrastructure
Local Manufacturers’ Focus
Local manufacturers prioritize certain aspects to maintain their competitive edge:
- Quality control standards
- Precision engineering
- Energy-efficient sensor designs
This technological leadership positions Germany as a crucial hub for smart sensor innovation, particularly in industrial and automotive applications. The country’s commitment to research excellence and practical implementation creates a dynamic ecosystem for sensor technology advancement.
Japan’s Smart Sensor Market: R&D and Industrial Adoption
Japan’s industrial sector is a leader in smart sensor innovation. The country’s technological ecosystem has produced groundbreaking developments in:
- Miniaturization Technology: Japanese firms lead in developing ultra-compact sensors for smartphones and wearables
- Energy-Efficient Sensors: Advanced power management systems reducing consumption by up to 40%
- High-Precision Manufacturing: Sensors capable of nanometer-level accuracy for industrial applications
Growth of Smart Sensor Adoption in Japan
The adoption rate of smart sensors across Japanese industries shows remarkable growth:
- Automotive: 78% implementation rate
- Manufacturing: 65% integration in production lines
- Healthcare: 45% adoption in medical devices
- Consumer Electronics: 82% market penetration
Specialized Sensor Applications by Japanese Companies
Japanese companies like Omron and Keyence have pioneered specialized sensor applications:
- Real-time quality control systems
- Predictive maintenance solutions
- Environmental monitoring networks
- Smart building management systems
Collaboration Between Research Institutions and Private Sector
Research institutions, including the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), collaborate with private sector partners to develop next-generation sensor technologies. These partnerships have resulted in breakthroughs in quantum sensing and bio-compatible sensor materials.
Japan’s Focus on Reliability and Precision
The Japanese market distinguishes itself through its focus on reliability and precision, with quality control standards exceeding global benchmarks by 15-20%. This commitment to excellence has established Japan as a crucial hub for high-performance smart sensor development and manufacturing.
Future Outlook: Innovations in Smart Sensor Technology
The world of smart sensors is about to undergo significant changes thanks to new technologies that have the potential to transform various industries. Here are some key innovations we can expect to see:
1. Quantum Sensing Technology
This technology utilizes quantum mechanical effects to achieve ultra-precise measurements. It offers enhanced sensitivity for detecting gravitational, magnetic, and electromagnetic fields, making it valuable in applications such as medical imaging and geological surveying.
2. Bio-Inspired Smart Sensors
These sensors are designed to mimic human sensory capabilities, allowing them to perceive their environment in a similar way. Additionally, self-healing materials will be used to extend the lifespan of these sensors, while adaptive learning capabilities enable them to adjust to changes in their surroundings.
3. Nano-Scale Developments
Advancements at the nanoscale level will lead to the creation of microscopic sensors capable of monitoring cellular processes. Through nano-engineering techniques, power consumption will be significantly reduced, making these sensors suitable for integration with biological systems in healthcare applications.
4. Edge Computing Integration
By incorporating edge computing into sensor technology, real-time data processing can occur directly at the sensor level. This eliminates the need for sending large amounts of data to centralized servers, resulting in reduced latency for decision-making systems and enhanced privacy through localized data handling.
These technological advancements are expected to open up new possibilities across various industries:
- Healthcare: Implantable sensors with quantum-level accuracy for precise monitoring of vital signs or disease progression.
- Manufacturing: Self-calibrating sensors equipped with predictive maintenance capabilities to minimize downtime and optimize production processes.
- Environmental Monitoring: Networks of nano-sensors deployed throughout ecosystems for accurate tracking of climate variables such as temperature, humidity, and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Transportation: Bio-inspired sensors integrated into autonomous vehicles for improved navigation and obstacle detection.
- Smart Cities: Integrated sensor networks powered by edge computing that enable efficient management of resources like energy consumption and waste disposal.
Research indicates that these innovations will drive two key trends in sensor technology:
- Miniaturization: Sensors will become smaller and more compact without compromising their functionality.
- Increased functionality: New features and capabilities will be added to existing sensor types through advanced materials or design techniques.
Furthermore, there is an expectation that power requirements for these sensors will decrease due to breakthroughs in energy harvesting methods or low-power communication protocols.
The combination of quantum technology (which leverages principles from physics), nanotechnology (focusing on manipulating matter at an atomic scale), and bio-inspired design principles (drawing inspiration from nature) holds great promise for revolutionizing how we sense our environment.
Competitive Landscape: Leading Players in the Smart Sensor Market
The smart sensor market has several key players who are influencing industry standards through strategic actions and technological advancements.
-
Texas Instruments – United States
-
Honeywell – United States
-
Bosch – Germany
-
STMicroelectronics – Switzerland
-
Panasonic Corporation – Japan
-
Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation – Japan
-
Omron Corporation – Japan
-
Murata Manufacturing – Japan
-
Samsung Electronics – South Korea
-
Renesas Electronics – Japan
Overall
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Global Smart Sensor Market Report |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Segment by Type |
|
| Segment by Application |
|
| Geographies Covered |
|
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
The smart sensor market is undergoing a significant transformation and is expected to reach $67.16 billion by 2025. This growth is driven by the increasing use of smart sensors in various industries and applications.
Key Market Dynamics
- 17.6% CAGR growth rate from 2025-2033
- Strong innovation centers in the U.S., Germany, and Japan
Factors Driving Market Expansion
- Rising demand for IoT and connected devices
- Advancement in AI and machine learning capabilities
- Growing industrial automation needs
- Increased focus on environmental monitoring
While there are challenges such as high installation costs and data security concerns, the smart sensor industry continues to evolve through technological innovations and partnerships. Companies are investing heavily in research and development to stay competitive.
The future of smart sensors depends on their ability to provide:
- Enhanced real-time monitoring capabilities
- Improved energy efficiency
- Greater integration with emerging technologies
- Advanced data analytics solutions
This growth indicates a significant shift for industries adopting smart sensor technologies, leading to improved efficiency and new applications across various sectors.
Global Smart Sensor Market Report(Can Read by Free sample)–Table of Contents
Chapter 1:Smart Sensor Market Analysis Overview
- Competitive Forces Analysis(Porter’s Five Forces)
- Strategic Growth Assessment(Ansoff Matrix)
- Industry Value Chain Insights
- Regional Trends and Key Market Drivers
- Smart Sensor Market Segmentation Overview
Chapter 2:Competitive Landscape
- GlobalSmart Sensor Players and Regional Insights
- Key Players and Market Share Analysis
- Sales Trends of Leading Companies
- Year-on-Year Performance Insights
- Competitive Strategies and Market Positioning
- Key Differentiators and Strategic Moves
Chapter 3:Smart Sensor Market Segmentation Analysis
- Key Data and Visual Insights
- Trends,Growth Rates,and Drivers
- Segment Dynamics and Insights
- Detailed Market Analysis by Segment
Chapter 4:Regional Market Performance
- Consumer Trends by Region
- Historical Data and Growth Forecasts
- Regional Growth Factors
- Economic,Demographic,and Technological Impacts
- Challenges and Opportunities in Key Regions
- Regional Trends and Market Shifts
- Key Cities and High-Demand Areas
Chapter 5:Smart Sensor Emerging and Untapped Markets
- Growth Potential in Secondary Regions
- Trends,Challenges,and Opportunities
Chapter 6:Product and Application Segmentation
- Product Types and Innovation Trends
- Application-Based Market Insights
Chapter 7:Smart Sensor Consumer Insights
- Demographics and Buying Behaviors
- TargetAudience Profiles
Chapter 8:Key Findings and Recommendations
- Summary of Smart Sensor Market Insights
- Actionable Recommendations for Stakeholders
Access the study in MULTIPLEFORMATS
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1-866-739-3133
Email: infor@wkinformation.com
What are the upstream and downstream dynamics of smart sensors?
The upstream and downstream dynamics of smart sensors involve understanding the supply chain, including how upstream factors like manufacturing and technology development influence market trends, while downstream factors pertain to market impact, pricing, and availability.
How is IoT integration influencing the smart sensor market?
IoT integration plays a crucial role in enhancing the functionality of smart sensors, enabling them to communicate data effectively and operate within interconnected systems, which drives demand across various applications.
What challenges are associated with the growth of smart sensors?
Key barriers affecting the growth of smart sensors include high installation costs, regulatory compliance challenges, and concerns regarding data security and compatibility with existing legacy systems.
How do geopolitical factors affect smart sensor production and trade?
Geopolitical influences significantly impact production levels and trade agreements for smart sensors. Key manufacturing regions are affected by trade policies and international relations that can alter supply chains.
What types of applications utilize smart sensors?
Smart sensors are utilized across various sectors including healthcare, automotive, industrial automation, and consumer electronics. Each application sector leverages different types of sensors such as touch sensors and flow sensors to enhance efficiency.
What is the future outlook for innovations in smart sensor technology?
The future outlook for smart sensor technology includes predictions for emerging innovations driven by advancements in AI, MEMS technology, and IoT integration. These developments are expected to enhance capabilities across multiple applications.

