$527 Million Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Market to Revolutionize Electronics and Telecommunications in the U.S., South Korea, and China by 2025
Explore key trends in the low-dielectric glass fiber market for 2025, including 5G adoption, manufacturing advancements, and industry growth in telecom and aerospace.
- Last Updated:
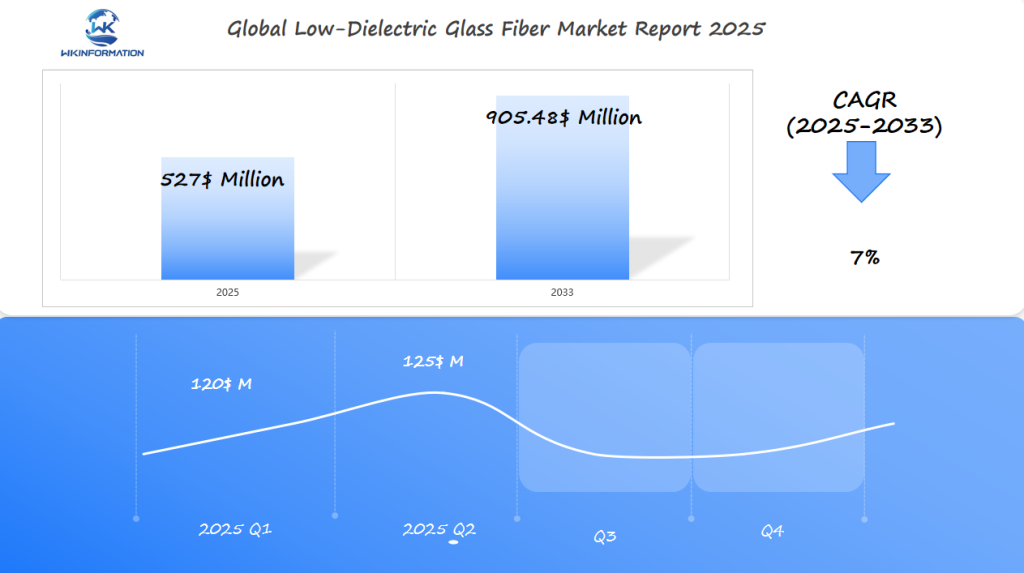
Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Market Q1 and Q2 2025 Outlook
The low-dielectric glass fiber market is expected to reach $527 million in 2025, with a 7% CAGR from 2025 to 2033. In Q1 2025, the market is anticipated to generate about $120 million, as the use of low-dielectric glass fibers in telecommunications, automotive, and consumer electronics accelerates. The demand for these materials is driven by their high performance in advanced applications, such as 5G networks and high-frequency electronics. The U.S., South Korea, and China are poised to lead the market. In South Korea, the rise of cutting-edge electronic devices and automotive technology will significantly boost the demand for low-dielectric glass fibers.
China, as a manufacturing powerhouse, will continue to drive demand due to its extensive telecommunications infrastructure and large-scale production of consumer electronics. By Q2 2025, the market is expected to grow to around $125 million, as South Korea’s electronics industry, along with China’s growing tech sector, continues to create strong demand.
Exploring the Upstream and Downstream Industry Chains for Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber
Exploring the Upstream and Downstream Industry Chains for Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber
The upstream and downstream industry chains for low-dielectric glass fiber involve a series of interconnected processes, starting from raw material extraction to the final application in advanced electronics and communications.
Upstream Industry Chain
-
Raw Materials Supply
-
Silica Sand, Alumina, Boron Oxide, Calcium Carbonate, and Magnesium Oxide are key inputs for producing specialized glass compositions with low dielectric constants.
-
Suppliers of high-purity chemical materials are critical at this stage to ensure electrical performance.
-
-
Glass Fiber Manufacturing
-
The raw materials are melted in high-temperature furnaces and drawn into fine filaments.
-
Specialized formulations and precise manufacturing conditions are necessary to achieve the low-dielectric properties.
-
Major players use proprietary technologies to optimize thermal stability and electrical insulation.
-
Downstream Industry Chain
-
Intermediate Processing
-
The drawn fibers are woven into fabrics or formed into prepregs (pre-impregnated materials).
-
These are then combined with resins (such as epoxy or polyimide) to create laminates for PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards).
-
-
Applications in End-Use Industries
-
Electronics and Semiconductor Packaging: Used in high-frequency circuit boards for 5G, smartphones, and IoT devices.
-
Aerospace and Automotive Electronics: Where high signal integrity and low dielectric loss are essential.
-
Data Centers and High-Speed Computing: Critical for maintaining high-speed data transmission with minimal signal delay.
-
Key Trends in the Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Market: Materials for Electronics
Electronics innovation is changing how we use materials like low-dielectric glass fiber. Now, makers focus on materials that are both good and affordable. They aim to make electronics faster, lighter, and more reliable.
Recently, there’s a move towards materials that cut down on signal loss but keep their heat stability.
1. Material Engineering Breakthroughs
New composites mix glass fiber with ceramics. This makes them better at handling heat without getting too heavy.
2. Sustainability Focus
Making these materials in eco-friendly ways reduces waste. They still keep their dielectric performance.
3. High-Frequency Applications
For 5G and wearable tech, Rogers RO4000 and DuPont’s PTFE are leading the way.
| Material Type | Key Advantages | Applications |
| FR-4 | Cost-effective, flame-resistant | PCBs for consumer electronics |
| PTFE | Low loss tangent | Radar systems, aerospace |
| Rogers RO4000 | High thermal conductivity | 5G base stations, medical imaging |
These advancements are driving electronics innovation. They make devices smaller and let them handle more data. As 5G grows, companies like Taiyo Nippon Glass and Corning are working hard to improve glass fiber for new uses.
There’s also a move towards simpler designs for IoT and cars. This keeps low-dielectric materials key in solving today’s tech problems.
Challenges in the Production and Sourcing of Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber
Making low-dielectric glass fiber is very precise. But, making it is hard because of bad raw material quality. It’s hard to find pure silica, so companies have to rely on a few suppliers. This makes the supply chain unstable, affecting glass fiber trends worldwide.
Key Challenges
- Raw material scarcity limits mass production
- High-precision equipment raises costs
- Logistics delays for international shipments
A table comparing production factors shows clear patterns:
| Factor | Impact |
| Material purity | Rises costs by 15-20% |
| Equipment scalability | Slows factory expansions |
| Global shipping | Adds 2-3 weeks to delivery times |
These problems are changing glass fiber trends to focus on making things closer to where they’re used. Companies like Corning and NEG are using new tech to make things better. But, finding a balance between quality and cost is still a big challenge for 5G.

Geopolitical Influence on the Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Market
Trade policies and political tensions affect how companies get materials. Issues like tariffs and sanctions cause sourcing challenges that mess up global supply chains. This makes production more expensive and slower due to export restrictions and trade barriers.
| Region | Key Issue | Impact |
| US-China | Technology Sanctions | Restricted material exports slow production |
| EU | Environmental Laws | Compliance delays |
| Asia-Pacific | Border Disputes | Limited supplier options |
Companies need to find new ways to get materials because of these sourcing challenges. For example, US companies pay more because of China’s export controls. EU producers have to follow strict recycling rules, which adds steps to getting materials. In Asia, conflicts limit access to important raw materials.
These issues make businesses rethink how they source materials globally. Political tensions directly impact the cost and availability of low-dielectric glass fiber. This pushes companies to work with local partners to avoid problems. Keeping the market stable means finding a balance between political risks and material needs.
Types of Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber: Types and Properties
Low-dielectric glass fibers come in many types, each with its own chemical makeup and manufacturing process. The main types are E-glass, S-glass, and quartz-based. Each type has its own cost, performance, and use:
| Use E-glass | 3.5-6.0 | Consumer electronics, automotive wiring |
| S-glass | 3.2-4.0 | High-frequency telecom equipment |
| Quartz-based | 3.7-4.2 | Radar systems, aerospace components |
Sources of Quartz-Based Fibers and Their Impact
Quartz-based fibers often come from areas rich in silica, like the Middle East and North Africa. This affects global markets and trade. For example, these regions’ quartz reserves can change production costs and trade deals.
Factors Engineers Consider When Choosing Materials
Engineers must think about these factors when picking materials for projects. This includes 5G infrastructure and defense technology.
Cost vs Performance Needs in Deciding Between E-Glass and S-Glass
Deciding between E-glass and S-glass depends on cost versus performance needs.
Trade Disputes and Their Effect on Quartz Variants
Quartz variants are better for precise uses but can be affected by trade disputes.
Risk Mitigation Strategies of Companies in the Face of Potential Trade Issues
Companies like NEG and Chongqing Fiberglass have spread out their suppliers to avoid risks.
Applications of Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber in Electronics, Telecommunications, and Aerospace
Low-dielectric glass fiber technology is changing the game in many fields. In electronics, it’s used in printed circuit boards (PCBs) for super-fast data transfer. Boeing and Lockheed Martin use it in aerospace to cut down signal loss in aircraft systems.
Big names like Verizon and AT&T count on these fibers for their 5G networks. Their low dielectric constant means data moves faster with less interference. Here are some key uses:
| Sector | Application | Example |
| Electronics | High-frequency circuit boards | Used in 5G routers and radars |
| Aerospace | Flight control systems | Boeing 787 wiring harnesses |
| Telecom | Undersea cables | Microsoft’s Project Natick data centers |
- Electronics: Reduces signal delay in gaming consoles and IoT devices
- Telecom: Enhances 5G tower efficiency across urban areas
- Aerospace: Critical for satellite antennas and navigation systems
These fibers also boost reliability in medical devices like MRI machines. They’re great for automotive radar systems in self-driving cars. As 5G grows, so will the need for these fiber technology properties, pushing innovation in U.S. tech.
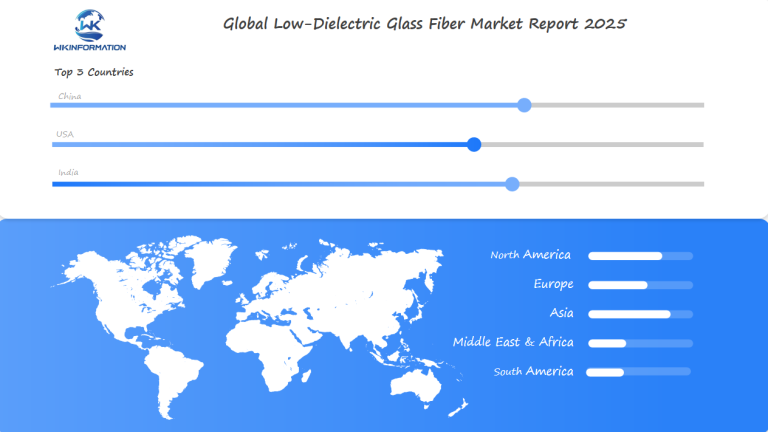
Global Insights into the Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Market
The global demand for low-dielectric glass fiber is on the rise, driven by telecommunications applications and advanced electronics pushing the boundaries of innovation. Asia-Pacific is leading the charge with its quick adoption of 5G infrastructure. Meanwhile, North America is focusing on research and development partnerships. Europe is putting a strong emphasis on sustainable manufacturing processes.
Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Telecommunications Applications
- Asia-Pacific: accounting for 40% of global production, fueled by 5G network expansions in China and India.
- North America: U.S. tech firms investing in low-dielectric materials for high-speed data transmission.
- Europe: EU regulations prioritizing eco-friendly manufacturing, boosting demand for sustainable fiber solutions.
Collaborations between Japanese and German manufacturers exemplify the global tech sharing spirit. South Korea’s advancements in aerospace and telecom applications also influence worldwide standards. As 5G expands, telecommunications applications remain a core focus for market players.
Future growth depends on international partnerships and adapting to regional needs. Emerging markets in Latin America and the Middle East are adopting these materials for smart city infrastructure and telecom upgrades.
U.S. Market Demand for Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber in Electronics Manufacturing
The U.S. electronics sector is a major player in the global market for low-dielectric glass fiber. The rise of 5G and advanced tech like wearables drives demand. Companies like Apple and Cisco need these fibers for faster, lighter devices, increasing U.S. production needs.
Key Drivers of Demand
- Tech Innovation: U.S. firms invest in R&D to integrate fibers into next-gen chips and antennas.
- Production Needs: Automakers and aerospace giants like Boeing use the material for high-speed data systems, fueling demand.
- Consumer Expectations: U.S. buyers expect reliable, high-performing electronics, pushing suppliers to adopt premium materials.
Global data shows 40% of U.S. fiber demand comes from consumer electronics. This matches federal efforts to boost domestic tech supply chains. Suppliers like Corning Inc. see more orders from U.S. clients making IoT devices and AI hardware. The U.S. market’s focus on quality and innovation leads the way globally.
South Korea’s Role in Low-Dielectric Fiber Technologies and Telecom Expansion
South Korea is leading the way in low-dielectric glass fiber tech. This is pushing telecom and electronics forward. Big names like Samsung Electronics and LG Chem are pouring money into research and development. They’re making materials that are key for 5G networks and fast data transfer.
Their work helps the U.S. electronics manufacturing sector. It’s because they need the latest parts for gadgets and industrial tools.
South Korean companies are teaming up with U.S. tech giants like Apple and Cisco. This is making fiber tech better for global use. They’re working on materials that are light, strong, and meet high standards.
For instance, Samsung teamed up with Qualcomm in 2023. They worked on making fiber tech better for 5G antennas. This move helped the U.S. electronics manufacturing sector stay competitive.
Investment in Fiber Tech R&D
- South Korea spent $1.2 billion on fiber tech R&D in 2022. They’re aiming at telecom and car markets.
- Now, 30% of global low-dielectric fiber exports come from joint ventures with U.S. companies.
South Korean innovators are making U.S. electronics manufacturing better. They’re helping make devices faster and more reliable. Their focus on green production also matches U.S. goals for sustainability. This creates chances for growth in both markets.
China’s Growing Market for Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber in 5G and Electronics
China’s need for low-dielectric glass fiber is growing fast with the rise of 5G. This material helps reduce signal interference, crucial for fast networks and advanced electronics. The “Made in China 2025” policy boosts tech innovation, leading to more production.
5G infrastructure advancements
Big industries are pouring money into making fiber. Places like Guangdong and Jiangsu are now making parts for phones and telecom gear worldwide. Experts think Chinese companies might export up to 40% of their products by 2025.
South Korea’s big telecom names like Samsung and SK Telecom are teaming up with Chinese makers. They want to find a balance between cost and quality. Chinese companies like Henkel Electronics and HTC Materials are also growing their R&D to meet global standards.
- 5G base stations need low-dielectric materials for high-frequency signals.
- China’s 2023-2025 tech plan sets aside $12 billion for fiber optic innovation.
As 5G networks spread worldwide, China is becoming a key player. This shift changes the game, offering chances for partnerships across borders. It also puts pressure on traditional suppliers.
The Future of Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber: Next-Gen Communication Technologies
Low-dielectric glass fiber is key for global communication systems. As China 5G growth speeds up, it will help with faster data and reliable connections. It’s expected to play a big part in 6G networks by 2030, making AI and IoT devices work together smoothly.
Expected Applications of Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber
Here are some of the expected applications of low-dielectric glass fiber in the future:
- Ultra-fast 6G networks with reduced signal loss
- Smart city infrastructure for real-time data transmission
- Autonomous vehicle systems requiring low-latency connections
Adoption and Forecast of Low-Dielectric Materials
The following table shows the adoption and forecast of low-dielectric materials in various technologies:
| Technology | 2024 Adoption | 2030 Forecast |
| 5G Base Stations | 45% | 90% (using low-dielectric materials) |
| IoT Devices | 22M units | 150M units |
China aims for 100% urban 5G coverage by 2030, boosting demand for advanced materials. New fiber coatings and nano-structured composites could cut production costs by 30%, studies show. Despite challenges, partnerships between telecoms and material suppliers are speeding up its use.
This material will link current 5G networks to new technologies. Its role in the digital future is clear—it’s making a connected, high-speed world possible.
Competitive Landscape in the Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Market
The top companies in the low-dielectric glass fiber market are competing fiercely to lead in next-gen communications technology. They are investing heavily in research and development to stay ahead of the competition.
Here are some of the key players in the industry:
- AGC Inc. – Japan
- 3B-the fibreglass company – Belgium
- Owens Corning – United States
- LANXESS – Germany
- Solvay – Belgium
- Jushi Group – China
- Sinoma Science & Technology Co., Ltd. – China
Other major companies such as Corning, Schott, and NGK Spark Plug are also actively involved in this market, working towards technological advancements and innovations.
Overall
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Global Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Market Report |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Segment by Type |
· E-glass · S-glass · Quartz-based |
| Segment by Application |
· Electronics · Telecommunications · Aerospace |
| Geographies Covered |
· North America (United States, Canada) · Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Russia) · Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan) · Southeast Asia (India) · Latin America (Mexico, Brazil) |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
Low-dielectric glass fiber continues to revolutionize electronics, telecommunications, and aerospace industries. In electronics, it enables faster data transmission and improved signal integrity in PCBs and high-frequency applications. The telecommunications sector benefits from enhanced 5G infrastructure and network performance, while aerospace applications see reduced signal loss and improved system reliability. As technology advances, the demand for low-dielectric glass fiber is expected to grow, particularly in emerging applications like IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and next-generation communication systems. The market’s future looks promising, driven by ongoing innovation, increasing digitalization, and the growing need for high-performance materials in critical applications.
Global Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Market Report (Can Read by Free sample) – Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Market Analysis Overview
- Competitive Forces Analysis (Porter’s Five Forces)
- Strategic Growth Assessment (Ansoff Matrix)
- Industry Value Chain Insights
- Regional Trends and Key Market Drivers
- Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Market Segmentation Overview
Chapter 2: Competitive Landscape
- Global Low-Dielectric Glass Fiberplayers and Regional Insights
- Key Players and Market Share Analysis
- Sales Trends of Leading Companies
- Year-on-Year Performance Insights
- Competitive Strategies and Market Positioning
- Key Differentiators and Strategic Moves
Chapter 3: Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Market Segmentation Analysis
- Key Data and Visual Insights
- Trends, Growth Rates, and Drivers
- Segment Dynamics and Insights
- Detailed Market Analysis by Segment
Chapter 4: Regional Market Performance
- Consumer Trends by Region
- Historical Data and Growth Forecasts
- Regional Growth Factors
- Economic, Demographic, and Technological Impacts
- Challenges and Opportunities in Key Regions
- Regional Trends and Market Shifts
- Key Cities and High-Demand Areas
Chapter 5: Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Emerging and Untapped Markets
- Growth Potential in Secondary Regions
- Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Chapter 6: Product and Application Segmentation
- Product Types and Innovation Trends
- Application-Based Market Insights
Chapter 7: Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Consumer Insights
- Demographics and Buying Behaviors
- TargetAudience Profiles
Chapter 8: Key Findings and Recommendations
- Summary of Low-Dielectric Glass Fiber Market Insights
- Actionable Recommendations for Stakeholders
Access the study in MULTIPLEFORMATS
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1-866-739-3133
Email: infor@wkinformation.com
What is low-dielectric glass fiber?
Low-dielectric glass fiber is a special material. It has low electrical conductivity. This makes it perfect for high-frequency electronics and telecommunications.
How is low-dielectric glass fiber used in electronics?
It’s mainly used in making printed circuit boards (PCBs), antennas, and other parts. These need minimal signal loss and high performance.
What market trends are influencing the low-dielectric glass fiber industry?
Trends include better materials engineering and more demand for 5G networks. Innovations also improve glass fiber’s properties and uses in tech.
What are the challenges in sourcing low-dielectric glass fiber?
Challenges include ensuring raw material quality, scaling production, and dealing with logistics. These can affect supply chains.
Which countries are leading in the production of low-dielectric glass fiber?
The U.S., South Korea, and China lead in production. They invest heavily and make significant advancements.
How does geopolitical influence affect the low-dielectric glass fiber market?
Trade policies, regulations, and tensions can disrupt supply chains. They also affect prices and give advantages to certain manufacturers.
What types of low-dielectric glass fibers are available?
There are many types, each with unique properties. They’re used in electronics, aerospace, and telecommunications.
What applications utilize low-dielectric glass fiber?
It’s used in telecommunications, high-frequency circuit boards, aerospace, and consumer electronics. Performance and reliability are key here.
How is the U.S. market for low-dielectric glass fiber evolving?
The U.S. market is growing. This is due to tech innovations, increased production needs, and high consumer expectations.
What role does South Korea play in low-dielectric fiber technologies?
South Korea is crucial. It invests in research, has advanced manufacturing, and strategic partnerships. This boosts its telecommunications and technologies.
How is China’s market for low-dielectric glass fiber growing?
China’s market is expanding fast. This is thanks to government support for 5G, increased demand for devices, and tech advancements in fiber production.
What does the future hold for low-dielectric glass fiber?
The future looks bright. Next-gen communication technologies will drive demand. Ongoing innovations will also improve material properties and uses.
Who are the key competitors in the low-dielectric glass fiber market?
Major players include global manufacturers and specialized companies, as illustrated in this image. They focus on tech advancements and strategic market positioning to seize new opportunities.

