Gas Insulated Switchgear Market Set to Exceed $5.37 Billion Globally by 2025 with Strong Demand in Japan, U.A.E., and the U.K.
Explore the future of the Gas Insulated Switchgear Market, poised to surpass $5.37 billion globally by 2025 amid rising demand.
- Last Updated:
Gas Insulated Switchgear Market Outlook for Q1 and Q2 2025
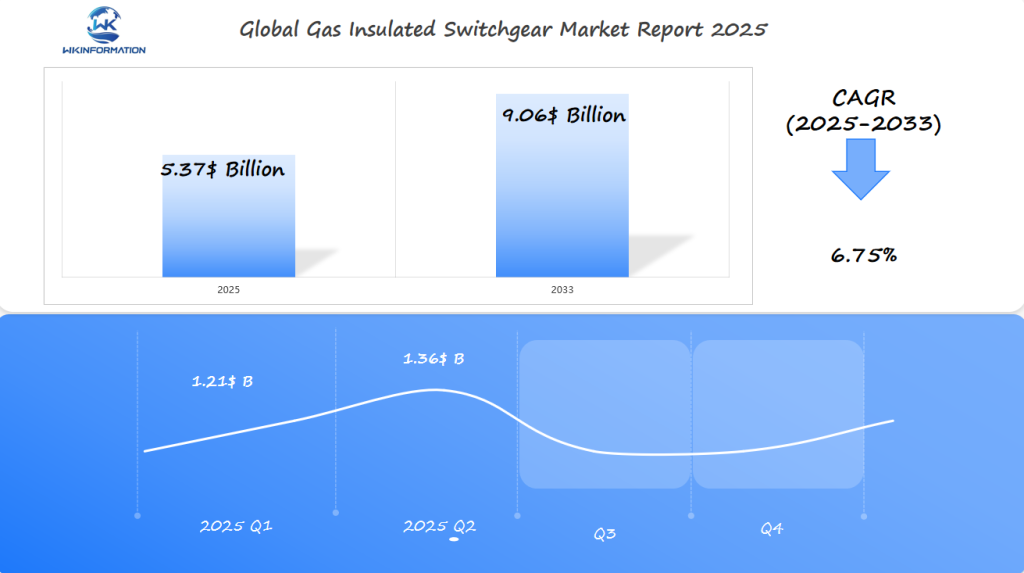
The Gas Insulated Switchgear market is projected to reach $5.37 billion in 2025, with a CAGR of 6.75% expected through 2033. Q1 2025 revenue is forecasted at approximately $1.21 billion, with Q2 rising to nearly $1.36 billion as utility-scale infrastructure projects and smart grid deployments continue to expand.
The increasing need for compact, safe, and high-capacity switchgear in urban substations and renewable integration projects is driving steady market growth. Japan, the U.A.E., and the U.K. are identified as key regional drivers, each investing in high-voltage transmission upgrades and advanced power infrastructure. These countries will play a vital role in shaping innovation and adoption trends within the GIS sector.
Understanding the Connection Between SF6 Procurement and Utility Deployment
Understanding the link between SF6 procurement and GIS deployment is crucial for stakeholders across the electrical supply chain. The production and deployment of GIS technology are closely tied to the availability and procurement of SF6 gas, a critical component used for insulation in GIS equipment.
SF6 Procurement and Its Impact on GIS Manufacturing
The procurement of SF6 gas is a significant factor in the manufacturing of GIS equipment. SF6 gas is used as an insulating medium due to its excellent dielectric properties. The availability and cost of SF6 can directly impact the production costs and timelines of GIS manufacturers.
Manufacturers must secure a stable supply of SF6 to meet the growing demand for GIS technology. This involves developing strategic partnerships with SF6 suppliers and investing in research and development to improve the efficiency of SF6 usage.
- Developing strategic partnerships with SF6 suppliers
- Investing in R&D to improve SF6 efficiency
- Exploring alternatives to SF6
Utility Deployment Strategies for GIS Technology
Utilities play a crucial role in the deployment of GIS technology. Their strategies for adopting GIS are influenced by factors such as grid modernization plans, regulatory policies, and the need for a reliable power supply.
Effective deployment strategies involve careful planning and assessment of the existing electrical infrastructure. Utilities must consider factors such as the age and condition of existing equipment, future demand projections, and the potential for integrating renewable energy sources.
By understanding the linkages between SF6 procurement and GIS deployment, stakeholders can better navigate the complexities of the GIS value chain and make informed decisions to support the growth of the electrical infrastructure.
Key Market Trends in Compact Design, Smart Grid Integration, and Reliability
As the GIS market grows, trends such as compact design and smart grid integration become increasingly important. The demand for efficient and reliable electrical infrastructure is driving innovation in GIS technology.
Compact Design and Its Advantages
Compact design is a significant trend in the GIS market, enabling utilities to install equipment in smaller spaces. This is particularly beneficial in urban areas where space is limited.
Advantages of Compact Design:
- Space efficiency
- Reduced installation costs
- Enhanced reliability
The compact design also contributes to the overall reliability of the GIS equipment by minimizing the risk of faults and reducing maintenance needs.
Smart Grid Integration and GIS Technology
The integration of GIS technology with smart grid initiatives is another key trend. Smart grids rely on advanced technologies to manage energy distribution efficiently.
The use of GIS in smart grids enables real-time monitoring and management of electrical networks, improving response times to faults and outages.
The reliability of GIS equipment is also a major focus, driven by the need for uninterrupted power supply in critical infrastructure. Manufacturers are continually improving the design and materials used in GIS equipment to enhance its reliability and lifespan.
Limitations Due to Environmental Concerns Over SF6 and Regulatory Shifts
Environmental concerns over SF6 have become a major limitation for the GIS market, driving regulatory shifts and industry responses. SF6, or sulfur hexafluoride, is a potent greenhouse gas used in GIS equipment for its insulating properties. However, its significant global warming potential has raised concerns among environmental agencies and regulatory bodies worldwide.
Environmental Concerns Related to SF6
The use of SF6 in GIS equipment has been a subject of increasing scrutiny due to its high global warming potential, which is approximately 22,800 times that of CO2 over a 100-year time frame. The main environmental concerns related to SF6 include its contribution to climate change, the challenges associated with its handling and disposal, and the potential for leaks during the manufacturing, installation, and operational phases.
Key Environmental Concerns:
- High global warming potential
- Challenges in handling and disposal
- Potential for leaks during manufacturing, installation, and operation
Regulatory Shifts and Their Impact on GIS Market
In response to the environmental concerns associated with SF6, regulatory bodies have begun to implement stricter regulations to limit SF6 emissions. These regulatory shifts are driving the GIS market towards the development and adoption of eco-friendly alternatives and more efficient GIS technologies.
For instance, the European Union has implemented the F-Gas Regulation, which aims to reduce the use of fluorinated gases, including SF6. Similarly, other countries are following suit with their own regulations and guidelines to minimize SF6 emissions.
| Region | Regulatory Measure | Impact on GIS Market |
| European Union | F-Gas Regulation | Reduction in SF6 usage, adoption of eco-friendly alternatives |
| United States | Voluntary SF6 reduction programs | Encouragement of best practices in SF6 handling and recycling |
| Japan | SF6 emission reduction guidelines | Promotion of SF6-free or low-SF6 GIS technologies |
The GIS market is responding to these regulatory shifts by innovating and adopting new technologies that minimize environmental impact. Manufacturers are developing SF6-free or low-SF6 GIS equipment, and utilities are exploring strategies to minimize SF6 leakage and improve recycling.
The future of the GIS market lies in its ability to adapt to these environmental concerns and regulatory shifts, embracing eco-friendly technologies and sustainable practices.

Geopolitical Risk and Supply Chain Disruptions Affecting Electrical Components
The global Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS) market is increasingly vulnerable to geopolitical risks and supply chain disruptions. These risks can significantly impact the availability and cost of critical components, affecting both manufacturers and end-users. As the demand for GIS technology continues to grow, understanding these challenges becomes crucial.
Risks and Their Impact on GIS Supply Chain
Geopolitical tensions, trade wars, and regional conflicts can disrupt the supply of raw materials and finished goods necessary for GIS production. For instance, restrictions on the import of certain materials can lead to shortages, delaying production and increasing costs. Companies involved in the GIS market must navigate these risks carefully to maintain their competitive edge.
Strategies to Mitigate Risks
To mitigate these risks, companies are adopting several strategies:
- Diversifying supply chains: This approach reduces dependence on any single region or supplier.
- Investing in local production: This strategy can help minimize the impact of international trade disruptions.
- Developing contingency plans: These plans enable companies to respond quickly to supply chain disruptions.
- Maintaining flexible manufacturing capabilities: This flexibility allows companies to adapt their production processes as needed.
By understanding the geopolitical landscape and its potential impacts on the supply chain, GIS manufacturers can better prepare for and navigate these challenges. This proactive approach is essential for maintaining a stable and competitive position in the global market.
Segmentation by Voltage Class, Installation Type, and Enclosure Configuration
The segmentation of the GIS market by voltage class, installation type, and enclosure configuration provides insights into its diverse applications. This segmentation is crucial for understanding the specific needs of different end-users and for manufacturers to tailor their products accordingly.
Voltage Class Segmentation
The GIS market is segmented into different voltage classes, ranging from low to high voltage.High-voltage GISis predominantly used in transmission and sub-transmission systems due to its ability to handle high electrical stresses. According to industry experts, “The demand for high-voltage GIS is driven by the need for reliable and efficient transmission systems.”
The voltage class segmentation is vital for determining the appropriate GIS for specific applications. For instance, high-voltage GIS is used in power transmission systems, while lower voltage GIS is used in distribution networks.
Installation Type and Enclosure Configuration
The installation type and enclosure configuration are other critical factors in GIS market segmentation. GIS can be installed indoors or outdoors, with each type having its specific requirements and advantages.
- Indoor GIS installations are typically used in urban areas where space is limited
- Outdoor GIS installations are used in substations and other outdoor facilities
The enclosure configuration varies from compact to modular designs, catering to different application needs.
- Compact GIS designs are preferred for their space-saving attributes
- Modular designs offer flexibility and scalability
Understanding these segments is essential for manufacturers to develop products that meet specific end-user needs and for end-users to select the most appropriate GIS solutions for their applications.
Application Analysis in Power Utilities, Industrial Plants, and Infrastructure
GIS technology is versatile and has a wide range of applications in power utilities, industrial plants, and infrastructure projects. It has become an essential tool in the electrical infrastructure sector, offering dependable and effective solutions.
GIS Applications in Power Utilities
In power utilities, GIS is used for transmission and distribution systems, improving the reliability and efficiency of electrical supply. GIS technology enables better management of electrical infrastructure, minimizing the chances of power outages and enhancing response times to faults.
GIS applications in power utilities
GIS applications in power utilities include:
- Network planning and optimization
- Asset management
- Outage management
- Integration with other utility systems
The image above illustrates various GIS applications in power utilities, showcasing how this technology is leveraged to enhance operations and service delivery.
GIS Applications in Industrial Plants and Infrastructure Projects
Industrial plants and infrastructure projects benefit significantly from GIS technology, particularly in terms of compact design and reliability. GIS systems are used to ensure the safe and efficient operation of electrical infrastructure within these environments.
| Application Area | Benefits of GIS |
| Industrial Plants | Reliable electrical supply, compact design |
| Infrastructure Projects | Efficient operation, enhanced safety |
The use of GIS in industrial plants and infrastructure projects is becoming increasingly common due to its ability to provide reliable and efficient electrical infrastructure. As the demand for electricity continues to grow, the adoption of GIS technology is expected to increase.
Global Regional Activity in Substation Modernization and Power Security
Regional trends in substation modernization are shaping the future of power security, with GIS technology playing a pivotal role. As the world shifts towards more sustainable energy solutions, the need for modernized substations has become increasingly important.
Regional Trends in Substation Modernization
Different regions are adopting various strategies for substation modernization, influenced by local grid infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, and technological advancements. For instance, in regions with aging infrastructure, the focus is on replacing outdated equipment with modern GIS solutions.
The use of GIS technology in substation modernization offers several benefits, including:
- Compact design, allowing for more efficient use of space
- Reliability and efficiency, reducing the likelihood of power outages
- Environmental benefits, as GIS technology can reduce the carbon footprint of substations
Power Security Initiatives
Power security initiatives are a critical component of substation modernization efforts. These initiatives aim to enhance the resilience and reliability of power grids, ensuring that they can withstand potential disruptions.
Key power security initiatives include:
- Implementing advanced monitoring and control systems
- Enhancing physical security measures to protect substations from potential threats
- Developing strategies for rapid response and recovery in the event of a power outage
By adopting these initiatives, regions can improve their power security, reducing the risk of disruptions and ensuring a more reliable supply of electricity.
Japan’s Advanced Grid and High Adoption of GIS Technologies
Japan has become a leader in using GIS technologies with its state-of-the-art grid system. The country’s advanced grid is built for reliability and efficiency, which in turn increases the need for top-notch GIS equipment.
Grid Modernization Efforts
Japan’s grid modernization efforts have been significant, with a focus on integrating advanced technologies like GIS into its electrical infrastructure. This has not only enhanced the reliability of the grid but also improved its overall efficiency.
GIS Adoption in Japan
The adoption of GIS technology in Japan has been widespread, with utilities and manufacturers alike recognizing its benefits. GIS technology offers several advantages, including compact design, high reliability, and reduced environmental impact.
Key Benefits of GIS Adoption in Japan:
- Reliability: GIS equipment is known for its high reliability, reducing the likelihood of power outages.
- Compact Design: GIS technology allows for more compact substations, making it ideal for urban areas.
- Environmental Benefits: GIS equipment is designed to minimize environmental impact, aligning with Japan’s environmental goals.
Here’s a comparison of GIS adoption in different regions of Japan:
| Region | GIS Adoption Rate | Key Drivers |
| Tokyo | 85% | High population density, need for reliable power supply |
| Osaka | 80% | Economic importance, grid modernization efforts |
| Hokkaido | 75% | Harsh climate, need for resilient infrastructure |
The data indicates a high adoption rate of GIS technology across various regions in Japan, driven by factors such as population density, economic importance, and the need for resilient infrastructure.
U.A.E.’s Infrastructure Expansion and Smart City Integration
U.A.E.’s ambitious infrastructure projects are transforming its urban landscape through smart city initiatives. The country’s vision for a sustainable and technologically advanced future is driving the adoption of innovative solutions like GIS technology.
The U.A.E. government has launched several initiatives aimed at developing smart cities, with a focus on efficient infrastructure, sustainable energy, and enhanced quality of life for residents. GIS technology plays a crucial role in these efforts by enabling the creation of compact, reliable, and efficient electrical infrastructure.
Infrastructure Expansion Plans
The U.A.E.’s infrastructure expansion plans are comprehensive, involving significant investments in transportation, energy, and telecommunications. These plans are designed to support the country’s growing population and economic development.
Key components of the U.A.E.’s infrastructure expansion include:
- Development of smart grids to manage energy distribution efficiently
- Expansion of public transportation systems for enhanced connectivity
- Investment in telecommunications infrastructure for high-speed data transmission
Smart City Initiatives and GIS Technology
GIS technology is integral to the U.A.E.’s smart city initiatives, providing the necessary infrastructure for efficient urban planning and management. By integrating GIS with other smart city technologies, the U.A.E. aims to create sustainable, livable cities.
The use of GIS technology in smart city projects enables:
- Efficient planning and management of urban infrastructure
- Enhanced reliability of electrical systems through advanced monitoring and control
- Sustainable development by optimizing resource utilization
In fact, these smart city initiatives are part of a larger push towards sustainability. This involves not just the implementation of advanced technologies but also a commitment to environmental sustainability.
Here’s a snapshot of the U.A.E.’s infrastructure expansion and smart city initiatives:
| Initiative | Description | Impact |
| Smart Grid Development | Advanced grid management for efficient energy distribution | Enhanced reliability and reduced energy losses |
| Public Transportation Expansion | Development of metro lines and bus networks | Improved connectivity and reduced congestion |
| Telecommunications Upgrade | Investment in high-speed data transmission infrastructure | Faster data transfer and enhanced connectivity |
U.K.’s Renewable Push and Upgrade of Aged Electrical Networks
The U.K. is working towards a greener future by upgrading its old electrical networks to support the growing need for renewable energy. This shift is essential for lowering carbon emissions and reaching the country’s sustainability objectives.
Renewable Energy Initiatives
The U.K. has been a leader in adopting renewable energy, making significant investments in wind and solar power. To effectively incorporate these renewable sources into the national grid, we need to upgrade our electrical networks so they can efficiently handle the fluctuating energy output.
GIS technology is crucial for this modernization effort. It offers a reliable and compact solution for substation infrastructure, enabling the smooth transmission and distribution of renewable energy.
Upgrading Aged Electrical Networks
As part of the grid modernization plan, we will be replacing outdated equipment with modern GIS systems. This upgrade will not only make the grid more reliable but also increase its capacity to accommodate the growing demand from renewable energy sources.
The use of GIS technology in the U.K.’s grid modernization efforts is backed by regulatory policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions. By implementing GIS, we can integrate more renewable energy into our grid and move closer to our sustainability goals.
The future of the U.K.’s energy landscape relies on successfully integrating renewable energy sources and upgrading our electrical infrastructure. With GIS technology leading the way, we are well on track to achieving a more sustainable energy mix.
Future Outlook on Eco-Friendly Alternatives and Smart Diagnostics
The GIS industry is about to undergo a transformation, driven by the need for eco-friendly alternatives to SF6 and the integration of smart diagnostics. As the world moves towards more sustainable practices, manufacturers are creating SF6-free GIS equipment, and utilities are looking for ways to reduce their environmental impact.
The Environmental Concern of SF6
SF6, a powerful greenhouse gas, has been a major environmental issue in the GIS industry. Eco-friendly alternatives are being developed to replace SF6, such as gases with lower global warming potential or other technologies that completely eliminate the use of SF6.
Eco-Friendly Alternatives to SF6
Researchers are actively looking for eco-friendly alternatives to SF6. Some of the options being explored include:
- Gases with lower global warming potential
- Alternative insulation materials
- SF6-free GIS designs
The goal of these alternatives is to minimize the environmental impact of GIS equipment while still delivering the same level of performance and reliability.
The Role of Smart Diagnostics in GIS
Smart diagnostics are changing the way GIS equipment is maintained and operated. By using digital technologies like IoT sensors and advanced data analytics, utilities can now:
- Monitor GIS equipment in real-time
- Predict potential failures
- Optimize maintenance schedules
This integration of smart diagnostics brings several benefits:
- Enhanced condition monitoring
- Predictive maintenance
- Improved system reliability and efficiency
As the GIS market continues to evolve, the adoption of eco-friendly alternatives and smart diagnostics is expected to play a crucial role in shaping its future outlook.
Competitive Mapping of OEMs and Innovation in GIS Technologies
- Hitachi – Japan
- Schneider Electric – France
- General Electric – United States
- Eaton Corporation – United States
- Toshiba – Japan
- Mitsubishi Electric – Japan
- Siemens Energy – Germany
- Hyosung Heavy Industries – South Korea
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited – India
- Powell Industries – United States
Overall
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Global Gas Insulated Switchgear Report |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Segment by Type |
· High Voltage Gas Insulated Switchgear · Medium Voltage Gas Insulated Switchgear |
| Segment by Application |
· Power Transmission Utility · Power Distribution Utility · Power Generation Utility · Infrastructure and Transportation · Industries & OEMs |
| Geographies Covered |
· North America (United States, Canada) · Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Russia) · Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan) · Southeast Asia (India) · Latin America (Mexico, Brazil) |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
The GIS market is growing due to the increasing need for reliable electrical infrastructure and the adoption of smart grid technologies. As the energy market continues to change, GIS technology will be crucial in shaping its future.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
The future outlook for the GIS market is promising, with emerging trends such as eco-friendly alternatives to SF6 and smart diagnostics gaining traction. These advancements are expected to drive innovation and efficiency in the industry.
As the world transitions towards a more sustainable energy future, the GIS market is likely to witness significant growth, driven by the need for efficient and reliable electrical infrastructure. With ongoing advancements in technology and strategic planning, the industry is well-positioned to address the challenges posed by environmental concerns and supply chain disruptions.
Global Gas Insulated Switchgear Market Report (Can Read by Free sample) – Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Gas Insulated Switchgear Market Analysis Overview
- Competitive Forces Analysis (Porter’s Five Forces)
- Strategic Growth Assessment (Ansoff Matrix)
- Industry Value Chain Insights
- Regional Trends and Key Market Drivers
- Women’s ActivewearMarket Segmentation Overview
Chapter 2: Competitive Landscape
- GlobalGas Insulated Switchgear players and Regional Insights
- Key Players and Market Share Analysis
- Sales Trends of Leading Companies
- Year-on-Year Performance Insights
- Competitive Strategies and Market Positioning
- Key Differentiators and Strategic Moves
Chapter 3: Gas Insulated Switchgear Market Segmentation Analysis
- Key Data and Visual Insights
- Trends, Growth Rates, and Drivers
- Segment Dynamics and Insights
- Detailed Market Analysis by Segment
Chapter 4: Regional Market Performance
- Consumer Trends by Region
- Historical Data and Growth Forecasts
- Regional Growth Factors
- Economic, Demographic, and Technological Impacts
- Challenges and Opportunities in Key Regions
- Regional Trends and Market Shifts
- Key Cities and High-Demand Areas
Chapter 5: Gas Insulated Switchgear Emerging and Untapped Markets
- Growth Potential in Secondary Regions
- Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Chapter 6: Product and Application Segmentation
- Product Types and Innovation Trends
- Application-Based Market Insights
Chapter 7: Gas Insulated Switchgear Consumer Insights
- Demographics and Buying Behaviors
- Target Audience Profiles
Chapter 8: Key Findings and Recommendations
- Summary ofWomen’s ActivewearMarket Insights
- Actionable Recommendations for Stakeholders
Access the study in MULTIPLEFORMATS
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1-866-739-3133
Email: infor@wkinformation.com
What is Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS) and how does it work?
Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS) is a type of electrical equipment used for switching and isolating electrical circuits. It uses sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas as an insulating medium to facilitate the transmission and distribution of electricity.
What are the benefits of using GIS technology?
GIS technology offers several benefits, including:
- Reduced environmental impact
- Enhanced safety
- Improved performance
It is also compact and reliable, making it ideal for urban areas and critical infrastructure.
What are the environmental concerns related to SF6 gas used in GIS equipment?
SF6 is a powerful greenhouse gas, and when it is released into the atmosphere, it contributes to climate change. As a result, regulatory changes are pushing the industry to adopt environmentally friendly alternatives and improve GIS technologies for better efficiency.
How is the GIS market segmented?
The GIS market can be segmented based on voltage class, installation type, and enclosure configuration. Voltage classes range from low to high voltage, and installation types include indoor and outdoor configurations.
What are the key trends shaping the GIS market?
Key trends shaping the GIS market include compact design, smart grid integration, and the need for reliable electrical infrastructure. The industry is also moving towards eco-friendly alternatives to SF6 and adopting smart diagnostics.
How is GIS technology used in power utilities, industrial plants, and infrastructure projects?
GIS technology is used in power utilities for transmission and distribution systems, in industrial plants for electrical infrastructure, and in infrastructure projects for compact and reliable electrical equipment.
What is driving the demand for GIS technology in regions like Japan and the U.A.E.?
Japan’s advanced grid infrastructure and the U.A.E.’s infrastructure expansion plans, driven by smart city initiatives, are driving the demand for GIS technology in these regions.
How is the GIS market expected to evolve in the future?
The GIS market is expected to evolve with a focus on eco-friendly alternatives to SF6 and advancements in smart diagnostics, enhancing the reliability and efficiency of GIS equipment.

