$54.85 Billion Surge in Fast Fashion Market by 2025: Growth Across the U.S., China, and India
Discover insights into the fast fashion market’s explosive growth to $54.85 billion by 2025, exploring key trends in sustainability, digital innovation, and global market dynamics across the U.S., China, and India. Learn how AI, circular economy models, and changing consumer behaviors are reshaping the industry’s future.
- Last Updated:
Fast Fashion Market Q1 and Q2 2025 Forecast
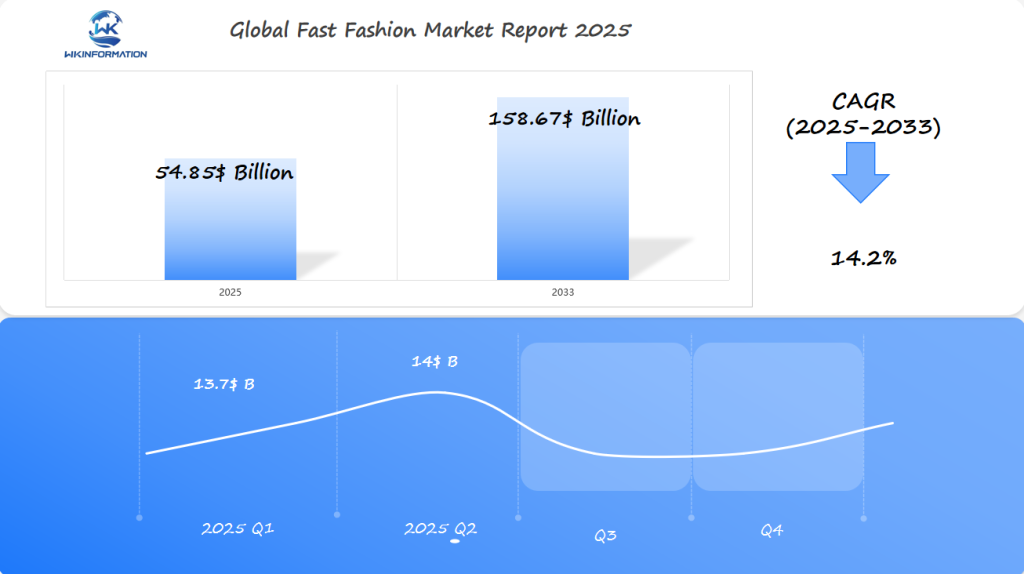
The Fast Fashion market, projected to reach $54.85 billion in 2025, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 14.2% from 2025 to 2033. In Q1 2025, the market is forecasted to generate around $13.7 billion, driven by the increasing demand for affordable, trendy apparel in the U.S., China, and India. The shift toward rapid production cycles and online shopping platforms will contribute to the growth of fast fashion in these key markets. Additionally, the rise of sustainable fashion and eco-conscious production will influence market dynamics, with more brands focusing on ethically produced garments.
By Q2 2025, the market is expected to reach $14 billion, with continued expansion in India and China, where the rise of middle-class consumers and a growing appetite for budget-friendly, trendy clothing will push growth further. The U.S. market will continue to dominate, driven by e-commerce platforms and the shift in consumer shopping behavior towards convenience and speed.
The Global Upstream and Downstream Industry Chains Driving Fast Fashion Growth
The fast fashion supply chain operates as a high-speed ecosystem designed to transform raw materials into trendy garments within weeks. This rapid transformation process relies on sophisticated upstream and downstream operations working in perfect synchronization.
Upstream Operations: Raw Materials to Manufacturing
- Fiber Production: Synthetic fibers like polyester dominate the market, accounting for 65% of raw materials due to cost-effectiveness
- Textile Manufacturing: Advanced manufacturing hubs in countries like Bangladesh and Vietnam process raw materials into fabrics
- Design and Prototyping: Tech-enabled design centers create multiple iterations of trending styles within days
Manufacturing Capabilities
- Automated cutting systems reduce fabric waste by 35%
- Digital printing technology enables rapid design changes
- Just-in-time production methods minimize inventory costs
- Strategic factory locations near shipping ports reduce transit times
Downstream Operations: Distribution to Consumer
The downstream segment of fast fashion operates through multiple channels:
- Direct-to-Consumer (D2C): Online platforms process orders within 24 hours
- Retail Networks: Strategic store locations in high-traffic areas
- Third-Party Marketplaces: Partnerships with e-commerce giants expand reach
- Social Commerce: Integration with social media platforms for instant purchasing
Supply Chain Integration
Real-time data analytics connect these elements:
- Inventory management systems track stock levels across locations
- Predictive algorithms forecast demand patterns
- Automated reordering systems maintain optimal stock levels
- Digital supply chain platforms coordinate multiple vendors
The success of fast fashion brands depends on their ability to manage these complex supply chain networks. Companies investing in vertical integration control both production and distribution channels, enabling faster market response times and better cost management.
This integrated approach allows brands to reduce the traditional 6-month fashion cycle to just 2-3 weeks, meeting consumer demands for the latest trends at competitive prices.
Key Trends in Fast Fashion: Speed, Affordability, and Sustainability
Fast fashion is evolving rapidly, driven by three key trends that are shaping the industry today: incredibly fast production, competitive pricing, and an increasing emphasis on sustainability.
1. Speed-to-Market Revolution
Brands are now able to bring their designs from concept to store shelves in a matter of weeks instead of months. This is made possible through:
- Real-time trend monitoring: Brands are using social media analytics to keep track of the latest fashion trends and consumer preferences.
- Quick response manufacturing: Manufacturers have implemented systems that allow them to quickly adjust their production processes based on changing demand.
- Flexible supply chains: Brands have established partnerships with suppliers and logistics providers that enable them to make rapid changes to their product offerings.
2. Affordability Drives Consumer Behavior
One of the main reasons why fast fashion has become so popular is its affordability. Fast fashion brands offer prices that are significantly lower than traditional retailers, making it easier for consumers to stay on top of the latest trends without breaking the bank. Here are some strategies that fast fashion brands use to keep their prices low:
- High-volume sales: Brands produce large quantities of each style, allowing them to negotiate better deals with manufacturers and suppliers.
- Regular promotions: Fast fashion brands often run sales and discounts to attract customers and encourage repeat purchases.
- Limited-time offers: Creating a sense of urgency through time-limited promotions encourages consumers to make immediate purchases.
3. Emerging Sustainability Initiatives
As awareness about environmental issues grows, many fast fashion brands are starting to incorporate sustainable practices into their operations. Here are some initiatives being adopted by the industry:
- Recycled materials: Brands are introducing collections made from recycled fabrics, reducing waste and promoting circularity in fashion.
- Water-saving processes: Manufacturers are implementing techniques that minimize water usage during production, addressing one of the industry’s biggest environmental concerns.
- Organic cotton: Some brands are transitioning from conventional cotton to organic cotton in their mainstream collections, reducing the use of harmful pesticides and promoting sustainable farming practices.
The speed at which fast fashion operates has reached new heights, with brands like Zara launching new collections every two weeks. Digital technology plays a crucial role in this by enabling quick identification of trends and rapid adaptation of designs. Additionally, automated manufacturing processes are significantly reducing production time.
Affordability remains a key factor attracting consumers to fast fashion. Brands are leveraging economies of scale to offer styles inspired by high-end runway looks at much lower prices. The average cost of a fast fashion item ranges from $10 to $30, making it accessible for a wider range of consumers.
Sustainability has become an important focus for the industry as well, driven by growing concern for the environment. Brands are now incorporating various eco-friendly practices such as:
- Using sustainable packaging materials
- Implementing clothing recycling programs
- Exploring alternative fabrics with lower environmental impact
- Developing strategies to reduce carbon emissions throughout their supply chain
The industry’s response to these trends can be seen in its innovative approaches towards production and marketing. For instance, digital sampling techniques are being used to minimize material waste during the design process while AI-powered demand forecasting helps prevent overproduction.
Brands are increasingly finding ways to balance speed and affordability with sustainability efforts, setting new standards within the industry that resonate with consumers’ values.
Challenges in Fast Fashion: Environmental Impact and Changing Consumer Preferences
The fast fashion industry faces significant environmental challenges that demand immediate attention. The production process generates approximately 10% of global carbon emissions, surpassing international aviation and maritime shipping combined.
Key Environmental Impacts:
- 20% of global wastewater comes from fabric dyeing
- 85% of textiles end up in landfills annually
- 60% of clothing materials contain harmful synthetic fibers
- 1.5 trillion liters of water consumed yearly in production
Labor practices across manufacturing hubs reveal concerning patterns of worker exploitation. Workers in major production countries face:
- 12-16 hour workdays
- Unsafe building conditions
- Below-minimum wage compensation
- Limited access to basic workers’ rights
- Restricted union participation
Consumer awareness has triggered substantial shifts in purchasing behavior. Recent market research indicates:
Changed Consumer Priorities:
- 73% of millennials actively seek sustainable fashion brands
- 65% of consumers research company ethics before purchasing
- 48% prefer brands with transparent supply chains
- 52% demand fair labor practices certification
These evolving preferences push brands toward ethical practices. Companies implementing sustainable initiatives report:
- Increased customer loyalty
- Higher brand value perception
- Stronger market positioning
- Enhanced competitive advantage
The industry faces mounting pressure from environmental regulators. New legislation targets:
- Carbon footprint reduction
- Waste management protocols
- Chemical usage in production
- Supply chain transparency
- Worker safety standards
These challenges reshape the fast fashion landscape, pushing brands to innovate sustainable solutions while maintaining profitability. Leading companies invest in recycling technologies, ethical sourcing, and worker welfare programs to address these pressing concerns.

Geopolitical Impact on the Fast Fashion Market
Trade policies shape the fast fashion landscape through tariffs, import quotas, and international agreements. Recent shifts in global trade relations have created significant ripples across the industry:
U.S.-China Trade Tensions
- 25% tariffs on Chinese textile imports
- Increased manufacturing costs for major brands
- Accelerated supply chain diversification to countries like Vietnam and Bangladesh
Brexit Effects
- Disrupted EU-UK supply chains
- Higher logistics costs for British retailers
- New customs procedures affecting delivery times
Regional political stability directly impacts fast fashion operations through:
Supply Chain Security
- Political unrest in manufacturing regions causes production delays
- Border conflicts affect shipping routes
- Currency fluctuations influence procurement costs
Market Access Barriers
- Local content requirements
- Investment restrictions in emerging markets
- Varying labor regulations across regions
The fast fashion industry responds to these challenges through:
- Strategic factory relocations
- Local manufacturing partnerships
- Digital supply chain optimization
- Regional inventory management
Political relationships between major economies continue to reshape sourcing strategies. Companies now prioritize:
- Risk assessment in politically volatile regions
- Alternative manufacturing locations
- Strong local market presence
- Adaptable distribution networks
These geopolitical factors push fast fashion brands to develop more resilient and flexible operational models, affecting their expansion strategies and market penetration capabilities across different regions.
Types of Fast Fashion Brands: High-Street, Online-Only, and Luxury Spin-Offs
The fast fashion industry has several different types of retailers, each catering to specific market segments and consumer preferences:
1. High-Street Brands
These are physical retail stores that have a strong presence on the high street:
- H&M leads the physical retail space with strategic store locations
- Zara combines in-store experiences with digital integration
- Uniqlo focuses on basic essentials with quality materials
- Primark maintains competitive pricing through minimal advertising
2. Online-Only Platforms
These brands operate exclusively online and target younger consumers:
- ASOS captures younger demographics through mobile-first shopping
- Boohoo specializes in rapid trend replication
- Fashion Nova leverages social media influencer marketing
- Shein disrupts traditional pricing models with ultra-fast production
3. Luxury Spin-Offs
These are luxury brands that have introduced more affordable lines to compete with fast fashion:
- &Other Stories (H&M Group) offers premium quality at mid-range prices
- COS presents minimalist designs with higher-end materials
- Massimo Dutti (Inditex) bridges fast fashion with luxury aesthetics
- Arket focuses on sustainable luxury basics
Each category has its own strategies to stay competitive in the market. High-street brands invest in prime retail locations to create immersive shopping experiences. Online-only platforms use data analytics to predict trends and optimize inventory. Luxury spin-offs maintain quality standards while implementing fast fashion’s rapid production cycles.
The lines between these categories are becoming less clear as brands adopt hybrid models. High-street retailers are expanding their digital presence, online-only platforms are experimenting with pop-up stores, and luxury spin-offs are integrating sustainable practices to justify higher price points.
These retail categories reflect changing consumer preferences, from traditional in-store browsing to mobile shopping experiences. Brands across all categories are now prioritizing digital integration, sustainable practices, and quick trend adoption to stay competitive in this fast-paced market.
Applications of Fast Fashion in Retail, E-commerce, and Sustainable Fashion Initiatives
Fast fashion applications span multiple retail channels, each offering unique advantages for brands and consumers.
Physical Retail Stores
Physical retail stores create immersive shopping experiences through strategic visual merchandising and frequent inventory rotations, keeping customers engaged with new arrivals every few weeks.
E-commerce Platforms
E-commerce platforms revolutionize fast fashion through:
- Virtual Try-Ons: AI-powered technology allowing customers to visualize clothing items
- Personalized Recommendations: Data-driven suggestions based on browsing history
- Flash Sales: Limited-time offers creating urgency and driving quick purchases
- Social Commerce: Integration with social media platforms for seamless shopping
Sustainable Initiatives
Sustainable initiatives reshape traditional fast fashion practices:
- Rental Services: Subscription-based clothing rentals reducing individual consumption
- Resale Platforms: Brand-operated secondhand marketplaces extending product lifecycles
- Recycling Programs: In-store collection points for used garments
- Eco-friendly Packaging: Biodegradable materials and minimal packaging designs
Digital Innovation
Digital innovation drives efficiency in inventory management through:
- RFID Technology: Real-time tracking of stock levels
- Predictive Analytics: Demand forecasting reducing overproduction
- Smart Warehousing: Automated systems speeding up order fulfillment
These applications demonstrate fast fashion’s adaptability in meeting evolving consumer demands while addressing sustainability concerns.
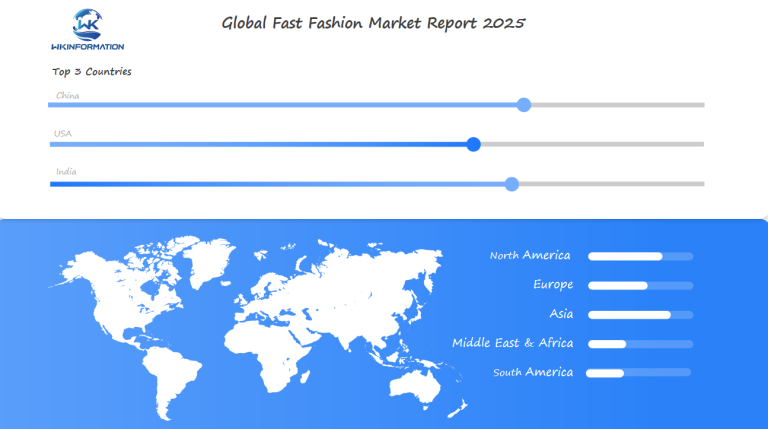
Global Insights into the Fast Fashion Market
The fast fashion market shows different patterns and consumer behaviors in various parts of the world. According to market research, it is expected to grow at a rate of 15.6% per year until 2025, but there will be significant differences in how quickly people adopt and buy these products.
Key Regional Characteristics
Here are some key characteristics of the fast fashion market in different regions:
- North America: High digital adoption rates drive online sales, with mobile shopping accounting for 70% of fast fashion purchases
- Europe: Strong presence of established brands, with sustainability concerns shaping consumer choices
- Asia-Pacific: Rapid urbanization fuels market expansion, particularly in second-tier cities
- Middle East: Growing youth population drives demand for western-style clothing
Variations in Market Penetration
Market penetration varies significantly across different types of markets:
- Mature Markets: Focus on digital innovation and sustainability
- Emerging Markets: Emphasis on physical retail expansion and localization
- Developing Markets: Building brand awareness and infrastructure
Price Sensitivity and Cultural Preferences
Price sensitivity differs across regions, with developed markets showing higher tolerance for premium fast fashion items. Cultural preferences play a crucial role in product adaptation, influencing:
- Design modifications
- Sizing standards
- Marketing strategies
- Seasonal collections
Influence of Social Media Trends
The fast fashion market is closely linked to social media trends, especially in areas where many people use smartphones. Local fashion influencers have a significant impact on regional preferences, creating small trends that fast fashion brands quickly include in their collections.
U.S. Fast Fashion Market: The Influence of Social Media and Consumer Behavior
Social media platforms have transformed the U.S. fast fashion industry, establishing a direct connection between popular styles and consumer buying choices. Platforms such as TikTok and Instagram are driving quick changes in fashion trends, with popular hashtags like #OOTD (Outfit of the Day) receiving billions of views and prompting immediate purchases.
Shopping Behavior of American Consumers
The shopping behavior of American consumers shows a clear pattern:
- Impulse Buying: 76% of U.S. fast fashion consumers make unplanned purchases influenced by social media
- Price Sensitivity: Young shoppers aged 18-24 prioritize affordability, spending an average of $40-60 per transaction
- Digital-First Shopping: 82% of U.S. fast fashion purchases now happen through mobile devices
How Fashion Influencers Impact Trends
Fashion influencers play a significant role in shaping market trends through various methods:
- Real-time style recommendations
- Try-on hauls
- Sharing discount codes
- Collaborating with brands
The Role of Social Commerce in Fast Fashion
The emergence of social commerce features such as Instagram Shopping and TikTok Shop has made it easier for consumers to make purchases. U.S. shoppers can now go from discovering a product to buying it in less than 60 seconds, resulting in quick turnover of inventory for brands.
The Constant Influence of Social Media on Fast Fashion Consumers
Data indicates that U.S. fast fashion consumers check social media an average of 6-8 times daily for style inspiration. This constant connectivity has compelled brands to maintain an active presence on social media, with some launching new styles every 24-48 hours to meet demand.
China's Fast Fashion Market: E-commerce Dominance and Domestic Growth
China’s fast fashion market is experiencing unprecedented growth due to its strong e-commerce infrastructure and changing consumer preferences. In 2023, the market value reached $83.4 billion, fueled by digital platforms like Tmall, JD.com, and emerging social commerce channels.
Key Factors Driving the Market:
- Mobile-first shopping behavior
- Integration of social media with e-commerce
- Rising middle-class disposable income
- Domestic brand competition
Local brands such as Shein and Urban Revivo have transformed the market by combining data-driven design with quick production cycles. These companies take advantage of China’s advanced manufacturing capabilities and complex supply chain networks to deliver popular styles within days.
Impact of Digital Innovation:
- Live streaming sales events generate 40% of fashion purchases
- AI-powered trend forecasting shapes inventory decisions
- Virtual try-on technology reduces return rates by 25%
- WeChat mini-programs enable seamless shopping experiences
The emergence of domestic fast fashion brands has created fierce competition for international players. Chinese consumers now prefer local brands that better understand their tastes and cultural subtleties. This change has forced established global retailers to adjust their strategies by incorporating local design elements and collaborating with Chinese influencers.
The growth of the market is supported by China’s advanced logistics system, which allows for same-day delivery in major cities and next-day delivery in most provinces. This efficiency in distribution has become a crucial competitive advantage for brands operating in the Chinese market.
India’s fast fashion market has great potential for growth, thanks to its young population and expanding middle class. The market takes global fashion trends and adapts them to suit local preferences, resulting in a unique combination of international styles with traditional Indian elements.
Key Factors Driving Growth:
- Rising disposable income among urban consumers
- Increased smartphone usage enabling mobile shopping
- Growing awareness of global fashion trends
- Expansion of organized retail sectors
The Indian market has its own distinct way of approaching fast fashion. Local brands like FabIndia and Global Desi have successfully combined modern designs with traditional Indian features, creating a new category of “Indo-western” fashion that appeals to young consumers.
How the Market is Adapting:
- Size adjustments to fit Indian body types
- Color choices aligned with regional preferences
- Incorporation of traditional prints and motifs
- Seasonal changes for local weather conditions
E-commerce platforms are playing a vital role in the growth of the market, with companies like Myntra and Flipkart leading the way in digital fashion retail. These platforms have introduced innovative features such as virtual try-ons and AI-powered style recommendations to improve the online shopping experience.
There is also significant growth happening in tier-2 and tier-3 cities, where better logistics networks and digital payment systems have made fashion more accessible. Local manufacturers are increasing their operations to meet the rising demand, creating efficient supply chains that shorten delivery times and reduce costs.
India’s Fast Fashion Market: Expanding Consumer Base and Local Adaptations
India’s fast fashion market has great potential for growth, thanks to its young population and expanding middle class. The market takes global fashion trends and adapts them to suit local preferences, resulting in a unique combination of international styles with traditional Indian elements.
Key Factors Driving Growth:
- Rising disposable income among urban consumers
- Increased smartphone usage enabling mobile shopping
- Growing awareness of global fashion trends
- Expansion of organized retail sectors
The Indian market has its own distinct way of approaching fast fashion. Local brands like FabIndia and Global Desi have successfully combined modern designs with traditional Indian features, creating a new category of “Indo-western” fashion that appeals to young consumers.
How the Market is Adapting:
- Size adjustments to fit Indian body types
- Color choices aligned with regional preferences
- Incorporation of traditional prints and motifs
- Seasonal changes for local weather conditions
E-commerce platforms are playing a vital role in the growth of the market, with companies like Myntra and Flipkart leading the way in digital fashion retail. These platforms have introduced innovative features such as virtual try-ons and AI-powered style recommendations to improve the online shopping experience.
There is also significant growth happening in tier-2 and tier-3 cities, where better logistics networks and digital payment systems have made fashion more accessible. Local manufacturers are increasing their operations to meet the rising demand, creating efficient supply chains that shorten delivery times and reduce costs.
Future Outlook for Fast Fashion: AI-Driven Design Innovations and Circular Economy Models
Artificial Intelligence is leading the way in the evolution of fast fashion, transforming design processes and production cycles. AI-powered algorithms analyze social media trends, runway shows, and consumer behavior to accurately predict upcoming fashion trends. This ability to foresee trends allows brands to shorten their design-to-production timelines from weeks to just a few days.
Key AI Applications in Fast Fashion:
- Design Generation: AI creates thousands of design variations based on trending elements.
- Pattern Optimization: Machine learning algorithms minimize fabric waste during cutting.
- Inventory Management: Smart systems predict demand patterns and optimize stock levels.
- Personalization: AI-driven recommendations enhance customer shopping experiences.
The integration of circular economy models is another significant change in the future of fast fashion. Brands are adopting innovative recycling programs and sustainable practices:
Circular Economy Initiatives:
- Textile-to-textile recycling technologies
- Rental and resale platforms within existing brand ecosystems
- Zero-waste manufacturing processes
- Blockchain-tracked supply chains for transparency
Leading fast fashion retailers have begun using AI-powered virtual try-on solutions and augmented reality shopping experiences. These technologies help reduce return rates, improve customer satisfaction, and decrease the environmental impact of reverse logistics.
The combination of AI technology and circular economy principles is giving rise to new business models in fast fashion. Subscription-based clothing services, powered by AI algorithms, offer personalized fashion selections while upholding circular principles through clothing rotation and recycling programs.
Digital fabric printing, made possible by AI color matching and pattern recognition, enables on-demand production, minimizing excess inventory and waste. This technology quickly adapts to shifting consumer preferences while still maintaining the rapid response times typical of fast fashion.
Competitive Landscape in the Fast Fashion Industry
The fast fashion market has several key players who influence industry trends and consumer expectations. H&M and Zara are at the forefront, setting industry standards with their efficient supply chains and quick design-to-store processes.
-
Inditex (Zara) – Spain
-
H&M Group – Sweden
-
Shein – China
-
Forever 21 – United States
-
GAP Inc. – United States
-
Primark (AB Foods) – United Kingdom
-
Uniqlo (Fast Retailing) – Japan
-
Mango – Spain
-
Boohoo Group PLC – United Kingdom
-
ASOS PLC – United Kingdom
Overall
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name |
Global Fast Fashion Market Report |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
| Segment by Type |
· High-Street · Online-Only · Luxury Spin-Offs |
| Segment by Application |
· Retail · E-commerce · Sustainable Fashion Initiatives |
| Geographies Covered |
· North America (United States, Canada) · Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Russia) · Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan) · Southeast Asia (India) · Latin America (Mexico, Brazil) |
| Forecast units |
USD million in value |
| Report coverage |
Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
The fast fashion industry continues to evolve across retail, e-commerce, and sustainable initiatives, adapting to changing consumer demands and technological advancements. Physical stores provide tangible shopping experiences while e-commerce platforms offer convenience and accessibility. The integration of sustainable practices reflects growing environmental consciousness.
As digital innovation reshapes the industry, successful brands will be those that effectively balance speed-to-market, affordability, and sustainability while maintaining strong omnichannel presence. The future of fast fashion lies in embracing technological solutions, sustainable practices, and consumer-centric approaches across all retail channels.
Global Fast Fashion Market Report (Can Read by Free sample) – Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Fast Fashion Market Analysis Overview
- Competitive Forces Analysis (Porter’s Five Forces)
- Strategic Growth Assessment (Ansoff Matrix)
- Industry Value Chain Insights
- Regional Trends and Key Market Drivers
- Fast FashionMarket Segmentation Overview
Chapter 2: Competitive Landscape
- Global Fast Fashionplayers and Regional Insights
- Key Players and Market Share Analysis
- Sales Trends of Leading Companies
- Year-on-Year Performance Insights
- Competitive Strategies and Market Positioning
- Key Differentiators and Strategic Moves
Chapter 3: Fast Fashion Market Segmentation Analysis
- Key Data and Visual Insights
- Trends, Growth Rates, and Drivers
- Segment Dynamics and Insights
- Detailed Market Analysis by Segment
Chapter 4: Regional Market Performance
- Consumer Trends by Region
- Historical Data and Growth Forecasts
- Regional Growth Factors
- Economic, Demographic, and Technological Impacts
- Challenges and Opportunities in Key Regions
- Regional Trends and Market Shifts
- Key Cities and High-Demand Areas
Chapter 5: Fast Fashion Emerging and Untapped Markets
- Growth Potential in Secondary Regions
- Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Chapter 6: Product and Application Segmentation
- Product Types and Innovation Trends
- Application-Based Market Insights
Chapter 7: Fast Fashion Consumer Insights
- Demographics and Buying Behaviors
- Target Audience Profiles
Chapter 8: Key Findings and Recommendations
- Summary ofFast Fashion Market Insights
- Actionable Recommendations for Stakeholders
Access the study in MULTIPLEFORMATS
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1-866-739-3133
Email: infor@wkinformation.com
What is driving the projected $54.85 billion growth in the fast fashion market by 2025?
The projected growth in the fast fashion market is driven by several factors, including increased consumer demand for trendy and affordable clothing, advancements in supply chain management, and the rise of e-commerce platforms. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for industry stakeholders.
How does the fast fashion supply chain contribute to its rapid growth?
The fast fashion supply chain plays a vital role in facilitating quick production and distribution. Key upstream factors include efficient raw materials sourcing and manufacturing capabilities, while downstream influences involve effective distribution channels that meet consumer demand for fashionable clothing.
What are the main characteristics that define fast fashion?
Fast fashion is characterized by its speed of production and affordability. Brands aim to deliver the latest trends at low prices, making fashionable clothing accessible to a wide audience. Additionally, there is a growing trend towards incorporating sustainability practices in response to environmental concerns.
What environmental challenges are associated with the fast fashion industry?
The fast fashion industry faces significant environmental challenges, including high carbon emissions and substantial textile waste. Labor practices in low-cost manufacturing countries also raise ethical concerns, prompting a shift in consumer preferences towards brands that prioritize sustainability.
How do geopolitical factors impact the fast fashion market?
Geopolitical factors such as trade policies and regional political stability significantly affect the growth trajectory of fast fashion brands. These elements influence supply chain operations and can either facilitate or hinder market expansion across different regions.
What future trends are expected to shape the fast fashion industry?
Future trends in the fast fashion industry include the integration of artificial intelligence to enhance design processes, allowing for faster turnaround times on new collections. Additionally, circular economy models focusing on recycling initiatives are anticipated to promote sustainability within the sector.

