Coal Market Set to Reach $8.93 Billion by 2025: Accelerating Demand in the U.S., China, and India
A comprehensive analysis of the coal market dynamics, examining upstream and downstream operations, key trends, growth factors, and market outlook through 2025. Explores global coal consumption patterns, industry challenges, geopolitical influences, and the evolving competitive landscape, with particular focus on major markets including the U.S., China, and India.
- Last Updated:
Coal Market Q1 and Q2 2025 Forecast
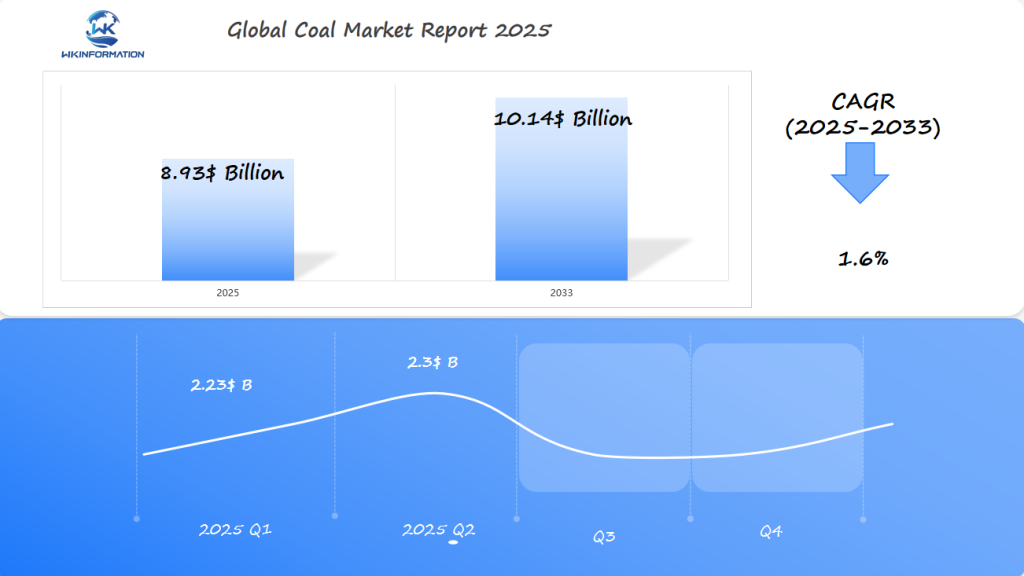
The Coal market is projected to reach $8.93 billion in 2025, with a CAGR of 1.6% from 2025 to 2033. In Q1 2025, the market is expected to generate around $2.23 billion, as coal consumption remains significant, especially in steel production and power generation. The U.S., France, and Brazil will continue to account for a large portion of global demand, though growth will be slower due to the global shift toward renewable energy sources.
By Q2 2025, the market is projected to grow to approximately $2.3 billion, with continued reliance on coal in certain regions, particularly in developing economies. The Brazilian coal industry will likely see a slight uptick as local demand for thermal coal for electricity generation rises, though global trends favor greener alternatives.
Understanding the Coal Market: Upstream and Downstream Factors
The coal market is influenced by a variety of activities that occur both before and after the mining process. These activities, known as upstream and downstream operations, play a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of the industry.
What are Upstream Operations?
Upstream operations refer to the activities involved in the early stages of the coal supply chain. This includes:
- Exploration: The process of searching for new coal deposits and assessing their viability.
- Mining: The extraction of coal from underground or surface mines.
- Raw Material Extraction: The acquisition of other resources needed for coal production, such as water or chemicals.
What are Downstream Activities?
Downstream activities encompass the processes that take place after coal has been mined. These include:
- Processing: The refinement and preparation of coal for use in various industries.
- Distribution: The transportation of coal to different locations, including power plants and manufacturing facilities.
- End-User Consumption: The final stage where coal is used by industries such as electricity generation or steel production.
Key Players in the Coal Supply Chain
Several key players are involved in both upstream and downstream operations:
- Upstream Players:Mining companies (e.g., BHP, Glencore, Peabody Energy)
- Equipment manufacturers
- Raw material suppliers
- Transportation providers
- Downstream Players:Power generation companies
- Steel manufacturers
- Industrial facilities
- Coal trading companies
The efficiency of the supply chain directly impacts coal prices and availability. Transportation costs, particularly rail and shipping expenses, can make up a significant portion (up to 60%) of the delivered price of coal. Any disruptions in the supply chain, such as adverse weather conditions or limitations in infrastructure, can lead to immediate fluctuations in prices.
Critical Factors Affecting the Supply Chain
Several factors play a crucial role in determining the efficiency of the coal supply chain:
- Mining capacity and production rates
- Quality of transportation infrastructure
- Availability of storage facilities
- Efficiency of port terminals
- Variations in regional demand
Recent global events have shed light on the vulnerabilities within this supply chain. Issues such as port congestion, shortages of shipping containers, and labor disruptions have resulted in delays in deliveries and spikes in prices. These challenges highlight the importance of having strong supply chain management strategies to maintain stability in the market.
Key Trends Driving the Coal Industry's Growth
The global coal industry’s growth is influenced by three main factors:
1. Rising Demand in Major Economies
- U.S. thermal coal markets show stabilization with increased power generation needs
- China maintains strong demand driven by industrial manufacturing expansion
- India’s rapid urbanization creates sustained demand for both thermal and metallurgical coal
2. Strategic Shift in Coal Types
The market witnesses a distinct evolution in coal preferences:
- Thermal coal dominates power generation sectors
- Metallurgical coal gains traction in steel manufacturing
- High-grade coal varieties command premium prices due to environmental regulations
3. Infrastructure Development Impact
Infrastructure projects across developing nations fuel coal demand:
- Transportation network expansions require steel production
- Urban development projects increase energy consumption
- Industrial zones creation boosts power requirements
The growth of the coal market reflects complex interactions between energy needs and economic development. China’s Belt and Road Initiative exemplifies how large-scale infrastructure projects drive coal demand. India’s ambitious industrial corridors similarly boost coal consumption through increased steel production and power requirements. The U.S. market demonstrates resilience through steady thermal coal demand for baseload power generation.
Barriers Impacting Coal Industry Expansion
The coal industry faces significant regulatory hurdles across major markets. In the United States, the Clean Air Act imposes strict emissions standards on coal-fired power plants, requiring substantial investments in pollution control technologies. Similar regulations in Europe under the European Green Deal mandate reduced carbon emissions, directly affecting coal operations.
Environmental concerns create substantial opposition to coal industry expansion:
- Air Quality Impact: Coal burning releases particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides
- Water Pollution: Acid mine drainage affects local water sources
- Land Degradation: Surface mining disrupts ecosystems and local communities
The rapid advancement of renewable energy technologies poses a direct challenge to coal’s market position. Solar and wind power costs have decreased by 85% and 65% respectively since 2010, making them increasingly competitive alternatives. Key renewable advantages include:
- Lower operational costs
- Minimal environmental impact
- Growing public support
- Government incentives and subsidies
Natural gas emergence as a cleaner-burning alternative has captured significant market share, particularly in power generation. Combined cycle gas turbines offer higher efficiency rates and lower emissions compared to traditional coal plants, attracting utilities seeking to meet environmental standards while maintaining reliable power supply.
The regulatory landscape continues evolving with carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions trading schemes implemented across various jurisdictions, adding operational costs to coal-dependent industries.

Geopolitical Factors Affecting Coal Production and Trade
The global coal market is currently facing major disruptions due to geopolitical factors. Here are some key dynamics at play:
U.S.-China Trade Tensions
The ongoing trade tensions between the U.S. and China have resulted in price fluctuations and uncertainty in the market. Chinese tariffs on U.S. coal imports have reached as high as 25%, making it more difficult for American producers to compete. As a result, many U.S. coal producers are now looking for alternative markets to sell their products, such as Southeast Asia and India.
Russia-Ukraine Conflict
The conflict between Russia and Ukraine has had a significant impact on European coal demand. European countries are now consuming more coal as they try to reduce their reliance on Russian natural gas. This shift in energy sources has led to several consequences:
- Increase in coal prices across European markets
- Renewed interest in domestic coal production
- Strengthened trade relationships with alternative suppliers like Australia and Indonesia
Trade Restrictions and Sanctions
Trade restrictions and sanctions imposed by various countries have created new dynamics in the coal market. Here are some effects of these measures:
Price Impact
- Supply chain disruptions are causing prices to rise by 15-20%
- Increased shipping costs due to rerouting of vessels
- Higher rates being charged for non-Russian coal supplies
Market Access Changes
- New trading routes are emerging as a result of sanctions
- Alternative supply chains are being developed
- Traditional buyer-seller relationships are shifting
Importance of the Asian Market
The Asian market, particularly China and India, has become increasingly important in determining global coal prices. China’s import policies and India’s demand patterns have a significant influence on pricing trends worldwide. Additionally, regional trade blocs and bilateral agreements now play a crucial role in determining market access and pricing structures.
Overall, these geopolitical factors are reshaping the coal industry, creating both challenges and opportunities for producers and traders alike.
Coal Market Segmentation: A Closer Look at Types
The coal market divides into distinct categories based on quality, usage, and chemical composition. Each type serves specific industrial purposes and commands different market values.
1. Thermal Coal (Steam Coal)
- Heat value: 5,000-8,000 kcal/kg
- Primary use: Electricity generation
- Key characteristics: High carbon content, moderate ash
2. Metallurgical Coal (Coking Coal)
- Heat value: 6,500-8,000 kcal/kg
- Primary use: Steel production
- Key characteristics: Low ash, low sulfur
3. Anthracite Coal
- Heat value: 7,000-9,000 kcal/kg
- Primary use: Industrial processes
- Key characteristics: Highest carbon content, lowest impurities
4. Sub-bituminous Coal
- Heat value: 4,000-5,500 kcal/kg
- Primary use: Power generation
- Key characteristics: Lower heating value, higher moisture
Market demand varies significantly across these types:
- Metallurgical coal commands premium prices due to its specialized use in steel production.
- Thermal coal represents the largest market segment by volume, driven by power generation needs.
- Anthracite, while representing a smaller market share, maintains steady demand in specialized industrial applications.
Quality parameters such as ash content, sulfur levels, and heating value directly influence pricing structures within each segment. These characteristics determine the coal’s suitability for specific applications and its market value.
The Role of Applications in Coal Demand
Coal applications shape market dynamics through two distinct categories: thermal coal for power generation and metallurgical coal for steel production.
Power Generation Applications
- Thermal coal powers approximately 36% of global electricity production
- Base-load power plants rely on coal for consistent energy output
- Advanced coal technologies enhance efficiency rates up to 45%
- Combined heat and power (CHP) systems maximize thermal coal utility
Steel Industry Requirements
- Metallurgical coal serves as a critical component in steel manufacturing
- High-grade coking coal achieves temperatures exceeding 1,100°C
- Steel mills require 770kg of coal to produce 1 ton of steel
- Premium hard coking coal commands higher market prices
Industrial Applications
- Cement manufacturing uses thermal coal for kiln operations
- Chemical industries extract coal derivatives for various products
- Paper mills depend on coal-generated steam for production
- Industrial boilers utilize thermal coal for process heat
The demand distribution between these applications varies by region:
- Asia-Pacific: 70% power generation, 25% steel production
- North America: 60% power generation, 30% industrial use
- Europe: 55% power generation, 35% steel manufacturing
Recent technological advancements in coal-fired plants have improved efficiency rates, while steel producers continue investing in coal-dependent blast furnaces, indicating sustained demand across both sectors.
Understanding the Global Coal Market
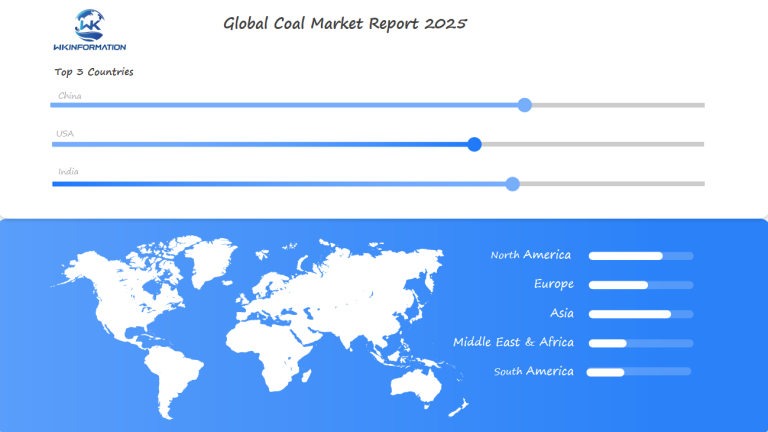
The global coal market shows significant differences in how different regions consume and produce coal. According to recent data, worldwide coal production reached 8.5 billion tonnes in 2022, with China responsible for half of this output. Indonesia and India have also seen steady growth in their production levels, reaching 687 million tonnes and 893 million tonnes respectively.
Global Coal Consumption Breakdown
When we look at global coal consumption, the numbers tell a complex story:
- Asia-Pacific Region: Consumes 80% of the world’s coal
- North America: Accounts for 8% of global coal consumption
- Europe: Represents 7% of global coal consumption
- Rest of World: Makes up 5% of global coal consumption
Predictions for Coal Consumption
Market forecasts suggest that coal consumption will peak in 2024, reaching around 8.5 billion tonnes. This milestone could indicate a potential shift in energy markets, which may have implications for:
- Price fluctuations in major coal-producing regions
- Investment trends in mining infrastructure
- Employment patterns in economies reliant on coal
Current Pricing Trends
Current pricing trends reflect the dynamics of the market:
- Thermal coal prices range from $175 to $200 per tonne
- Metallurgical coal prices range from $250 to $300 per tonne
- Prices vary by region based on quality and transportation costs
The Significance of the Anticipated Peak
The expected peak in 2024 is crucial for the industry as countries try to balance their energy security needs with environmental commitments. Market analysts predict a gradual decline in consumption after 2024, but prices are likely to stay above pre-pandemic levels due to ongoing industrial demand in key markets.
U.S. Coal Market: Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
The U.S. coal market is currently facing a complex situation with increasing demand for thermal coal despite changes in the energy industry. According to recent data, thermal coal consumption in power generation sectors has risen by 15%. This increase can be attributed to several factors:
- Higher prices of natural gas
- Increased demand for electricity
- Disruptions in the supply chain of alternative energy sources
Challenges Faced by U.S. Coal Producers
U.S. coal producers are encountering significant challenges in the market:
Regulatory Pressures
- Stricter environmental regulations
- Targets for reducing carbon emissions
- Clean energy mandates at the state level
Market Competition
- Price competition from natural gas
- Growing adoption of renewable energy sources
- Limited opportunities for exporting coal
Opportunities for Growth
Despite these challenges, there are several opportunities for growth:
- Technology Integration: Implementing advanced clean coal technologies and carbon capture systems
- Export Market Development: Establishing new trade partnerships with emerging economies
- Diversification: Expanding product offerings to include specialty coal products
Resilience in the Domestic Market
The domestic coal market is showing resilience through various means:
- Strategic reopening of mines in key production areas
- Investments in improving operational efficiency
- Development of reserves containing metallurgical coal
U.S. producers are adapting to the realities of the market by implementing strategies to reduce costs and exploring additional services that add value. These adaptations position the industry to maintain its importance in the national energy mix while navigating the transition towards cleaner energy sources.
China's Role in the Global Coal Market Growth
China’s power sector is the largest consumer of coal in the world. Its energy policies and consumption patterns have a significant impact on the global coal market. The demand for electricity in China continues to grow, and coal-fired power generation still makes up about 60% of its energy sources.
Key Energy Policy Impacts:
- Implementation of the “dual control” policy targeting energy consumption
- Strategic management of coal reserves to stabilize domestic prices
- Strict regulations on imports that affect international trade
Despite global pressure to reduce emissions, China’s coal-fired power generation capacity has remained strong, with new plants being built. The country’s power utilities ensure a steady demand for coal through:
- Long-term contracts with domestic miners
- Stockpiling during peak seasons
- Use of ultra-low emission technologies
Future Market Outlook:
The Chinese government’s focus on energy security means that it will continue to invest in coal infrastructure. Even though the country plans to become carbon neutral by 2060, the demand for coal in the short term will still be strong because of:
- Growth needs in the industrial sector
- Limited options for generating baseload power
- Economic priorities in developing areas
Recent changes in policy suggest that China is trying to find a balance between its environmental goals and energy security needs. Instead of immediately shutting down coal plants, China’s efforts to modernize its power sector are focused on improving efficiency. This indicates that the coal market will remain stable until 2025.
India's Growing Demand for Coal: Key Factors to Watch
India’s industrial sector expansion drives substantial growth in coal demand, particularly in steel manufacturing and power generation. The country’s infrastructure development initiatives, including the National Infrastructure Pipeline, require significant metallurgical coal supplies.
Key growth indicators in India’s coal market:
- Industrial Production: 7.8% growth in manufacturing output
- Steel Production: 125 million tonnes annual capacity
- Power Generation: 55% reliance on coal-fired plants
India maintains its position as the largest importer of Australian metallurgical coal, importing 85 million tonnes annually. This dependency stems from limited domestic coking coal reserves and quality requirements for steel production.
The supply dynamics present a complex picture:
- Domestic SupplyLimited high-quality reserves
- Production constraints
- Transportation bottlenecks
- Import RequirementsHigh-grade metallurgical coal
- Thermal coal for power plants
- Specialized grades for industrial use
The gap between domestic production and demand continues to widen. India’s coal imports are projected to reach 265 million tonnes by 2025, marking a 15% increase from current levels. The country’s state-owned Coal India Limited plans to boost domestic production, yet import dependency remains crucial for meeting quality specifications in steel manufacturing.
Recent policy changes support increased coal usage through streamlined mining licenses and improved transportation infrastructure. These initiatives aim to balance domestic production with import requirements while sustaining industrial growth.
Future Outlook for the Coal Market
The coal market’s trajectory beyond 2025 points to significant shifts in global consumption patterns. Market projections indicate a gradual decline in coal demand starting from 2025-2026, driven by:
- Accelerated adoption of renewable energy technologies
- Implementation of stricter environmental regulations
- Decreasing costs of alternative energy sources
- Technological advancements in energy storage solutions
The impact of the energy transition varies across regions:
Coal producers face substantial challenges adapting to this evolving landscape. Many are diversifying their portfolios through:
- Investment in clean coal technologies
- Development of carbon capture solutions
- Strategic asset repositioning
- Exploration of alternative revenue streams
Price volatility remains a key concern, with analysts predicting fluctuations between $60-80 per ton for thermal coal post-2025. The metallurgical coal segment displays resilience, maintaining stronger pricing due to limited substitutes in steel production.
Market dynamics suggest a two-speed transition, where:
- Advanced economies reduce coal dependency by 30-40% by 2030
- Developing nations sustain demand through industrial growth
- Regional markets fragment based on policy frameworks
- Supply chains reorganize to accommodate shifting demand centers
These changes reshape investment strategies across the coal sector, pushing companies toward sustainable practices while maintaining operational efficiency.
Competitive Landscape in the Coal Industry
The global coal industry is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and state-owned enterprises that dominate production and supply. Key players operate across various segments of the coal value chain—ranging from mining and processing to logistics and power generation.
-
BHP – Australia
-
Rio Tinto – United Kingdom / Australia (dual-listed)
-
China Shenhua Energy – China
-
Anglo American plc – United Kingdom
-
Coal India – India
-
NTPC Limited – India
-
Sasol – South Africa
-
Shaanxi Coal and Chemical Industry – China
-
Teck Resources – Canada
-
ČEZ Group – Czech Republic
Overall
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name |
Global Coal Market Report |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
| Segment by Type |
· Thermal Coal (Steam Coal) · Metallurgical Coal (Coking Coal) · Anthracite Coal · Sub-bituminous Coal |
| Segment by Application |
· Power Generation · Steel · Industrial |
| Geographies Covered |
· North America (United States, Canada) · Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Russia) · Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan) · Southeast Asia (India) · Latin America (Mexico, Brazil) |
| Forecast units |
USD million in value |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
The coal market remains a complex and dynamic industry driven by diverse applications and global demand patterns. Power generation continues to be the primary consumer of thermal coal, accounting for over a third of worldwide electricity production. The steel industry’s reliance on metallurgical coal maintains steady demand, with specific quality requirements shaping market prices and trade flows.
Industrial applications across cement, chemical, and paper manufacturing sectors provide additional market stability through diversified demand. While environmental concerns and energy transitions pose challenges, the coal market demonstrates resilience through technological advancements and efficiency improvements.
The future outlook suggests a gradual evolution rather than immediate disruption, with regional variations in consumption patterns and regulatory frameworks playing crucial roles. Understanding these market dynamics, along with upstream and downstream factors, remains essential for stakeholders navigating this vital energy resource sector.
Global Coal Market Report (Can Read by Free sample) – Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Coal Market Analysis Overview
- Competitive Forces Analysis (Porter’s Five Forces)
- Strategic Growth Assessment (Ansoff Matrix)
- Industry Value Chain Insights
- Regional Trends and Key Market Drivers
- CoalMarket Segmentation Overview
Chapter 2: Competitive Landscape
- Global Coalplayers and Regional Insights
- Key Players and Market Share Analysis
- Sales Trends of Leading Companies
- Year-on-Year Performance Insights
- Competitive Strategies and Market Positioning
- Key Differentiators and Strategic Moves
Chapter 3: Coal Market Segmentation Analysis
- Key Data and Visual Insights
- Trends, Growth Rates, and Drivers
- Segment Dynamics and Insights
- Detailed Market Analysis by Segment
Chapter 4: Regional Market Performance
- Consumer Trends by Region
- Historical Data and Growth Forecasts
- Regional Growth Factors
- Economic, Demographic, and Technological Impacts
- Challenges and Opportunities in Key Regions
- Regional Trends and Market Shifts
- Key Cities and High-Demand Areas
Chapter 5: Coal Emerging and Untapped Markets
- Growth Potential in Secondary Regions
- Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Chapter 6: Product and Application Segmentation
- Product Types and Innovation Trends
- Application-Based Market Insights
Chapter 7: Coal Consumer Insights
- Demographics and Buying Behaviors
- Target Audience Profiles
Chapter 8: Key Findings and Recommendations
- Summary ofCoal Market Insights
- Actionable Recommendations for Stakeholders
Access the study in MULTIPLEFORMATS
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1-866-739-3133
Email: infor@wkinformation.com
What are the upstream and downstream dynamics in the coal market?
In the coal market, upstream dynamics refer to the processes involved in coal production, including mining and extraction. Downstream dynamics encompass the distribution and consumption of coal, involving key players such as producers, distributors, and end-users. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for analyzing the overall coal supply chain.
What key trends are driving growth in the coal industry?
Key trends driving growth in the coal industry include increased demand in major economies like the U.S., China, and India, a shift towards thermal and metallurgical coal, and infrastructure projects that boost demand. These factors create a robust environment for coal consumption despite emerging challenges.
What barriers does the coal industry face for expansion?
The coal industry faces several barriers to expansion, including regulatory challenges that impose strict compliance measures, environmental concerns leading to public opposition against coal usage, and heightened competition from renewable energy sources which are gaining market share.
How do geopolitical factors influence coal production and trade?
Geopolitical factors significantly affect coal production and trade by influencing trade relations that impact prices and market access. For instance, tensions such as U.S.-China trade relations or the Russia-Ukraine conflict can alter European demand for coal and result in tariffs that affect U.S. coal imports.
What applications drive demand for different types of coal?
Demand for thermal versus metallurgical coal is driven by distinct applications. Thermal coal is primarily used in power generation, while metallurgical coal is vital for steel production. Current trends show increasing reliance on both types of coal depending on industrial needs and energy generation requirements.
What does the future outlook for the global coal market look like?
The future outlook for the global coal market suggests potential changes post-2025 due to shifting energy landscapes. While peak consumption is forecasted around 2024, long-term implications may include a decline in demand as countries transition towards cleaner energy sources, impacting producers significantly.

