$267.77 Million Electrostatic Chucks Market Accelerates in 2025: Japan, South Korea, and U.S. Lead Semiconductor Advancements
The $267.77M Electrostatic Chucks Market is accelerating in 2025, led by Japan, South Korea, and the U.S. Learn more about this growing industry.
- Last Updated:
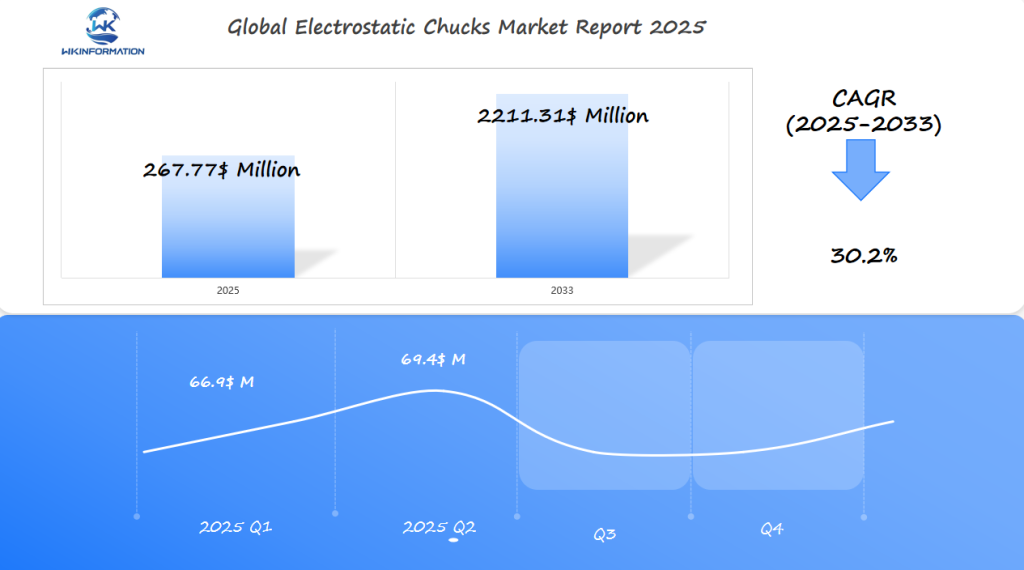
Electrostatic Chucks Market Q1 and Q2 2025 Forecast
The Electrostatic Chucks market is expected to reach $267.77 million in 2025, with a CAGR of 30.2% from 2025 to 2033. In Q1 2025, the market is projected to generate approximately $66.9 million, driven by significant demand in Japan, South Korea, and the U.S. as the semiconductor and electronics industries continue to expand. Electrostatic chucks play a critical role in wafer handling and surface mounting processes, particularly in semiconductor manufacturing where precision is essential.
By Q2 2025, the market is expected to reach $69.4 million, with growth propelled by advancements in semiconductor fabrication technologies and the increasing adoption of electrostatic chucks for automated processes in robotics and medical devices. The strong growth in semiconductor demand, particularly in Asia, will be a key driver, as countries like Japan and South Korea lead in technology production.
Understanding the Upstream and Downstream Supply Chains for Electrostatic Chucks
Efficiency in the electrostatic chucks supply chain is crucial for global semiconductor manufacturing. Let’s explore how raw materials transform into advanced components in factories worldwide.
The Upstream Supply Chain: From Raw Materials to Components
The upstream supply chain involves the production of basic materials that are essential for manufacturing electrostatic chucks. Here’s how it works:
- Material Suppliers: At the beginning of the process, suppliers provide fundamental materials such as ceramics and adhesives.
- Key Players: Companies like CoorsTek and SCHOTT specialize in offering high-purity ceramics that are vital for ensuring the strength of the chucks.
- Midstream Manufacturers: These raw materials then make their way to midstream manufacturers such as Semicon Equipment Group and Lam Research.
- Component Fabrication: In this stage, the midstream makers use these materials to mold them into functional chucks.
The Downstream Supply Chain: From Components to End-Users
The downstream supply chain focuses on the application of electrostatic chucks in semiconductor production. Here’s how it operates:
- Final Assembly: Once the chucks are fabricated, they are sent to final assembly processes where they are integrated into lithography tools.
- End-User Factories: Prominent semiconductor companies like TSMC and Samsung Foundry utilize these lithography tools equipped with chucks in their manufacturing facilities.
The Link Between Different Stages
The supply chain connects various stages involved in semiconductor production:
- Raw material mining ➔ Component fabrication ➔ Final assembly ➔ End-user factories
| Stage | Key Players | Role |
| Upstream | Ceramic suppliers | Material production |
| Midstream | Equipment manufacturers | Chuck assembly |
| Downstream | Semiconductor firms | Final product use |
The Impact of Disruptions
Any disruptions within this supply chain, such as silicon shortages, can have a significant impact on chip manufacturing globally. Understanding the electrostatic chucks supply chain provides insights into how materials and innovation influence technology industries.
Key Trends Driving the Electrostatic Chucks Market: Semiconductor and Display Industry Growth
Electrostatic chucks are key in today’s manufacturing, especially with semiconductor manufacturing growth on the rise. The need for smaller, faster chips for 5G and AI boosts the demand for precise wafer handling. This growth also pushes for chuck innovations to handle high temperatures and vacuum processes.
Main Factors Driving Semiconductor Manufacturing Growth
There are three main factors driving semiconductor manufacturing growth:
- Advancements in chip design that push factories to expand production lines.
- Increased investments in foundries across Asia, where most semiconductor manufacturing happens.
- Growth in display tech like OLED panels for smartphones and TVs, needing precise temperature control during production.
As the display industry moves towards flexible screens and higher-resolution panels, electrostatic chucks play a crucial role. They ensure uniform pressure during processing. This connection between semiconductors and displays creates a strong market for chucks. With global foundries expanding, the need for reliable chucks is key to keeping production efficient.
Challenges in Electrostatic Chucks Manufacturing and Material Innovations
Creating electrostatic chucks is a precise task. Manufacturing challenges include keeping materials uniform and handling heat. Engineers must balance conductivity and toughness, especially for new semiconductor needs.
Some of the key challenges include:
- Process variability in composite material bonding
- Cost constraints for high-purity ceramic components
- Ensuring consistent flatness in large wafer chucks
New innovations tackle these problems. Silicon carbide composites cut down on thermal stress. Additive manufacturing makes prototyping easier. AI checks for micro-cracks early.
New solutions like graphene-enhanced substrates and alloys with low thermal expansion are making chucks better. These steps help manufacturers meet the growing demand for semiconductors.

Geopolitical Influence on the Electrostatic Chucks Market
Global trade shapes the electrostatic chucks industry. Geopolitical impact on markets changes supply chains and demand. Trade tensions, like those between the U.S. and China, affect semiconductor manufacturing. This is a key area for electrostatic chucks.
Key Geopolitical Factors Affecting the Electrostatic Chucks Market
- Trade policies between Japan, South Korea, and the U.S. influence raw material exports critical for chucks.
- Sanctions and tech export controls disrupt production timelines for semiconductor firms reliant on these components.
- Regional conflicts accelerate R&D investments in domestic manufacturing to reduce reliance on geopolitical hotspots.
Recent U.S.-China trade disputes have shown global chip production’s vulnerabilities. For example, restrictions on semiconductor equipment exports forced some manufacturers to seek alternative suppliers for electrostatic chucks. This geopolitical impact on markets drives companies like Applied Materials and Tokyo Electron to diversify production hubs in politically stable regions.
Electrostatic Chucks Market by Type: Coulomb and Johnsen-Rahbek Systems
Electrostatic chucks use two main technologies: Coulomb and Johnsen-Rahbek systems. These systems have different designs and uses. They shape the market in semiconductor manufacturing.
1. Coulomb systems
Use electrostatic force to hold wafers. They are great for high-temperature processes. This makes them popular in lithography and etching equipment.
2. Johnsen-Rahbek systems
Mix mechanical clamps with electrostatic fields. They are stable in low-vacuum settings. This makes them common in LED and flat-panel displays.
The market for Johnsen-Rahbek systems grows with LED production. Coulomb systems benefit from advancements in semiconductor technology. Suppliers like Tokyo Electron and LAM Research make these systems for specific needs.
Manufacturers choose based on process needs. Coulomb is good for 300mm wafer lines because of its heat resistance. Johnsen-Rahbek is better in low-pressure environments.
Applications of Electrostatic Chucks in Semiconductor, LED, and Vacuum Processing
Electrostatic chucks (ESCs) are key in advanced manufacturing. They hold materials securely under harsh conditions. This makes them essential for semiconductor LED vacuum applications. Let’s see how they benefit three major industries:
Semiconductor LED Vacuum Applications
- Semiconductor Fabrication: In chip making, ESCs hold silicon wafers during plasma etching and deposition. This ensures no microchip defects and precise nanoscale work.
- LED Manufacturing: LED producers use ESCs to hold gallium nitride substrates at high temperatures. This boosts light efficiency and cuts down on waste.
- Vacuum Processing: In vacuum chambers, ESCs keep components stable during aerospace and medical device coating. Their non-magnetic design prevents interference with sensitive gear.
Experts at Tokyo Electron say ESCs reduce downtime by 40% in semiconductor cleanrooms. For vacuum work, Veeco depends on ESCs for ultra-high vacuum integrity during atomic layer deposition. These advancements boost the semiconductor LED vacuum applications supply chain, leading to cost savings and quality enhancements.
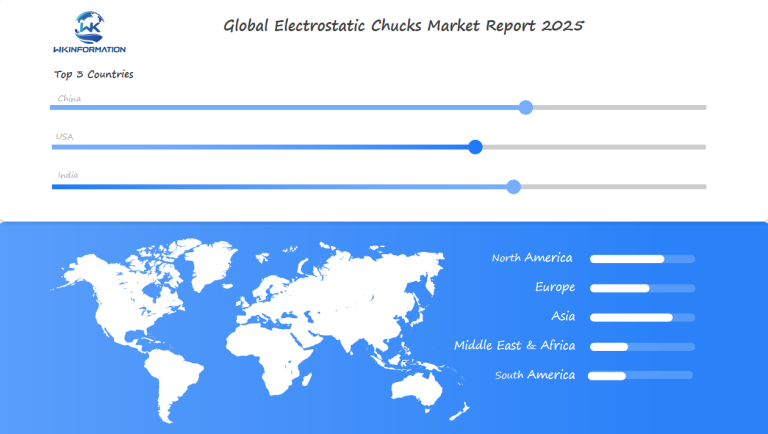
Global Insights into the Electrostatic Chucks Market
The global electrostatic chucks market is shaped by competition and new tech. Japan, South Korea, and the U.S. lead in production. But, new players from emerging economies are exploring new uses.
Innovations Driving Change
Innovations in materials like ceramic composites and advanced polymers are changing the game. These advancements help handle high-temperature processes better.
Regional Trends
- Asia-Pacific leads in adoption due to strong semiconductor output.
- North America focuses on R&D for AI-driven quality control systems.
- Europe explores eco-friendly materials to meet sustainability goals.
Supply Chain Dynamics
Supply chain shifts are also a big part of the story. Companies like Tokyo Ohka Kogyo and SK Materials are forming new partnerships. This is to secure raw materials and manage costs.
Price Factors
Price changes in silicon wafers and rare metals offer both challenges and chances for cost savings. This is crucial for keeping production affordable.
Future Collaborations
Looking to the future, we see more teamwork between big tech and startups. They’re working together to cut energy use and make chucks last longer for future chips. These efforts make electrostatic chucks key for meeting global chip needs by 2030 and beyond.
Japan’s Advanced Manufacturing of Electrostatic Chucks for Lithography and Etching
Japan is a leader in lithography expertise, driving semiconductor innovation globally. Companies such as Tokyo Electron and Hitachi High-Tech produce electrostatic chucks with exceptional precision. These chucks are essential components for high-quality lithography systems.
The Importance of Electrostatic Chucks in Semiconductor Manufacturing
In the process of chip manufacturing, wafers must be held in place with utmost stability during various stages of production. Any slight movement or misalignment can result in defects on the tiny circuits being etched or printed onto the wafer surface. This is where electrostatic chucks come into play.
Electrostatic chucks use electrical forces to securely hold the wafer without any mechanical contact. This non-contact gripping mechanism minimizes the risk of damage to delicate wafers and allows for precise positioning during critical processes like lithography and etching.
By ensuring that wafers remain perfectly stationary throughout these processes, electrostatic chucks contribute significantly to reducing defects and improving yield rates in semiconductor manufacturing.
Innovations Driving Japan’s Electrostatic Chuck Manufacturing
Japan’s success in manufacturing electrostatic chucks can be attributed to several key factors:
- Advanced materials: The use of cutting-edge ceramics with excellent thermal stability properties enables chucks to withstand extreme processing conditions encountered during chip fabrication.
- Automation: Incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) technologies into quality control measures allows for real-time defect detection and ensures consistent product excellence.
- Collaborations: Strategic partnerships with leading global semiconductor companies such as ASML and TSMC facilitate knowledge exchange and access to new markets.
| Company | Product | Key Application |
| Tokyo Electron | ECP-2000 Series | Lithography alignment systems |
| Hitachi High-Tech | Hi-CHUCK Pro | Etching chamber integration |
Meeting Industry Demands: Temperature Resilience for Advanced Etching
One of the significant challenges faced by semiconductor manufacturers is the increasing demand for smaller, more powerful chips. Technologies such as 5nm and 3nm node designs require intricate patterns to be etched onto silicon wafers with utmost precision.
To meet these requirements, Japan’s electrostatic chuck manufacturers are continuously innovating their products. Newer versions of chucks are being developed that can withstand higher temperatures—up to 400°C—during etching processes. This capability is crucial as certain advanced etching techniques involve exposing wafers to elevated temperatures for optimal results.
By investing in research and development efforts focused on temperature resilience, Japan aims to strengthen its position as a key player in cutting-edge semiconductor production.
Conclusion
Japan’s expertise in manufacturing electrostatic chucks plays a vital role in supporting global semiconductor innovation. Through advanced materials, automation, collaborations, and temperature resilience capabilities, Japanese companies are well-equipped to meet the evolving demands of the industry.
South Korea’s Expanding Semiconductor Sector and Demand for Electrostatic Chucks
South Korea’s tech industry is rapidly expanding, with major players like Samsung and SK Hynix leading the way. They have plans to invest $50 billion by 2030. This growth will create a greater demand for cutting-edge equipment such as electrostatic chucks used in chip manufacturing.
South Korea semiconductor expansion trends
Government support is crucial. Programs like the “K-Semiconductor Strategy” offer funding and help with research. This support helps companies use the latest technology, including electrostatic chucks. These tools are key for handling wafers during chip production.
Several factors are driving up demand:
- Rising 3D NAND and logic chip production
- Partnerships with equipment suppliers
- Focus on eco-friendly materials for chucks
Recent investments highlight the focus:
| Year | Investment Focus |
| 2023 | Advanced lithography tools |
| 2024 | Wafer fabrication facilities |
| 2025+ | AI-driven production systems |
This growth isn’t just about new tools. Collaborating with global leaders keeps South Korea at the forefront. Electrostatic chucks are now a key part of this progress, demonstrating the country’s commitment to technology. For instance, these electrostatic chucks play a significant role in handling wafers during chip production, thus highlighting their importance in the semiconductor sector.
U.S. Innovation in High-Performance Electrostatic Chucks for Wafer Processing
U.S. companies are leading in electrostatic chuck technology. They focus on wafer processing innovations to improve semiconductor making. Companies like Applied Materials and Lam Research spend a lot on research and development.
They create chucks that are more precise and efficient in heat. This helps a lot in making chips.
- Advanced ceramics reduce heat distortion for smaller, faster chips.
- AI-driven quality checks cut defects by monitoring chuck performance in real time.
- New adhesion technologies enable handling of ultra-thin wafers without cracking.
These innovations help U.S. companies meet the growing demand for advanced semiconductors. Working with places like MIT and Stanford speeds up new discoveries. This keeps the U.S. at the forefront of wafer processing innovations.
Customers get tools that save money and make production faster.
The Future of Electrostatic Chucks: Next-Generation Materials and AI Integration
The future of electrostatic chucks is bright, thanks to next-generation materials and AI integration. New materials like graphene-based composites and ceramic alloys are being developed. They promise better thermal stability and longer lifespans, solving old problems in high-temperature semiconductor processing.
Next-Generation Materials for Electrostatic Chucks
Companies like Applied Materials and Hitachi High-Tech are exploring next-generation materials. They aim to reduce substrate warping and improve uniformity. The benefits are clear:
- Enhanced resistance to extreme temperatures
- Lightweight designs for faster production cycles
- Lower material waste during fabrication
How AI Integration is Changing Quality Control
AI integration is changing quality control. Machine learning algorithms analyze real-time data from chucks. They predict wear patterns and adjust processes automatically. This reduces downtime and defects by up to 30%, as shown in 2024 trials.
The Role of AI in Adaptive Chucks
With AI, these materials will help chucks adapt to changing wafer conditions. Researchers at the University of Tokyo are working on adaptive chucks. These chucks use embedded sensors and AI models to self-calibrate. Early studies suggest they could cut chip defect rates by 40%.
These advancements make electrostatic chucks essential for making 3nm and 2nm chips. As the industry moves towards smaller sizes, the combination of next-generation materials and AI integration will lead to greater manufacturing efficiency.
Competitive Landscape in the Electrostatic Chucks Market
The Electrostatic Chucks (ESCs) market has a competitive landscape shaped by technological innovation, precision manufacturing, and the growing demand in semiconductor and flat panel display industries. Key players compete based on product performance, customization, reliability, and the ability to meet stringent cleanroom and thermal management standards. The market includes a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized niche manufacturers, with differentiation often focused on materials (ceramic vs. quartz), chucking methods (Coulomb vs. Johnsen-Rahbek), and application-specific solutions.
-
Entegris Inc. – United States
-
SHINKO Electric Industries Co., Ltd. – Japan
-
Kyocera Corporation – Japan
-
NGK Insulators, Ltd. – Japan
-
TOTO Ltd. – Japan
-
NTK CERATEC Co., Ltd. – Japan
-
Tsukuba Seiko Co., Ltd. – Japan
-
Lam Research Corporation – United States
-
Applied Materials Inc. – United States
-
II-VI M Cubed (part of Coherent Corp.) – United States
Overall
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Global Electrostatic Chucks Market Report |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Segment by Type |
· Coulomb Systems · Johnsen-Rahbek Systems |
| Segment by Application |
· Semiconductor · LED · Vacuum Processing |
| Geographies Covered |
· North America (United States, Canada) · Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Russia) · Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan) · Southeast Asia (India) · Latin America (Mexico, Brazil) |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
In semiconductor, LED, and vacuum processing, electrostatic chucks play a vital role in modern manufacturing. They provide precise wafer handling in semiconductor fabrication, enable efficient LED production processes, and ensure stable substrate holding in vacuum environments. The technology continues to evolve with both Coulomb and Johnsen-Rahbek systems finding specialized applications across these sectors.
As manufacturing demands grow more complex, ESCs remain fundamental to achieving the precision and reliability required in these critical industries. Their ongoing development and integration with advanced materials and control systems will further enhance manufacturing capabilities in these key technological sectors.
Global Electrostatic Chucks Market Report (Can Read by Free sample) – Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Electrostatic Chucks Market Analysis Overview
- Competitive Forces Analysis (Porter’s Five Forces)
- Strategic Growth Assessment (Ansoff Matrix)
- Industry Value Chain Insights
- Regional Trends and Key Market Drivers
- Electrostatic ChucksMarket Segmentation Overview
Chapter 2: Competitive Landscape
- Global Electrostatic Chucksplayers and Regional Insights
- Key Players and Market Share Analysis
- Sales Trends of Leading Companies
- Year-on-Year Performance Insights
- Competitive Strategies and Market Positioning
- Key Differentiators and Strategic Moves
Chapter 3: Electrostatic Chucks Market Segmentation Analysis
- Key Data and Visual Insights
- Trends, Growth Rates, and Drivers
- Segment Dynamics and Insights
- Detailed Market Analysis by Segment
Chapter 4: Regional Market Performance
- Consumer Trends by Region
- Historical Data and Growth Forecasts
- Regional Growth Factors
- Economic, Demographic, and Technological Impacts
- Challenges and Opportunities in Key Regions
- Regional Trends and Market Shifts
- Key Cities and High-Demand Areas
Chapter 5: Electrostatic Chucks Emerging and Untapped Markets
- Growth Potential in Secondary Regions
- Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Chapter 6: Product and Application Segmentation
- Product Types and Innovation Trends
- Application-Based Market Insights
Chapter 7: Electrostatic Chucks Consumer Insights
- Demographics and Buying Behaviors
- Target Audience Profiles
Chapter 8: Key Findings and Recommendations
- Summary ofElectrostatic ChucksMarket Insights
- Actionable Recommendations for Stakeholders
Access the study in MULTIPLEFORMATS
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1-866-739-3133
Email: infor@wkinformation.com
What are electrostatic chucks and how do they function?
Electrostatic chucks are used in making semiconductors and other precise work. They hold wafers and substrates without using mechanical clamps. They work by electrostatic force, which helps in keeping things clean and aligned during processes like lithography and etching.
What is driving the growth of the electrostatic chucks market?
The growth of the electrostatic chucks market is mainly due to the fast growth of semiconductors and displays. New technologies and bigger production needs are driving the demand for better electrostatic chucks. This is especially true in places like Japan, South Korea, and the U.S.
What challenges do manufacturers of electrostatic chucks face?
Making electrostatic chucks is tough. Companies struggle with keeping quality high, dealing with process changes, and finding new materials. They need to solve these problems to make better products and meet the industry’s needs.
How do geopolitical factors impact the electrostatic chucks market?
Politics and international relations can significantly affect the electrostatic chucks market. Changes in trade rules and laws can disrupt supply chains and market trends. It’s crucial for everyone involved to stay informed about global news.
What are the different types of electrostatic chucks available?
There are two main types: Coulomb and Johnsen-Rahbek systems. Coulomb systems are simple and reliable, while Johnsen-Rahbek systems offer better grip. Each type has its own strengths and uses.
Where are electrostatic chucks commonly used?
Electrostatic chucks play a crucial role in the production of semiconductors, LEDs, and vacuum processing. They securely hold substrates in place while maintaining their cleanliness, making them essential in these industries.
What technological advancements are influencing the future of electrostatic chucks?
New materials and artificial intelligence in making are changing electrostatic chucks. These advancements will make them work better and more efficiently. It’s an exciting time for the industry.
Why is Japan considered a leader in electrostatic chuck manufacturing?
Japan is a leader in producing electrostatic chucks due to its advanced technology and precision. The country prioritizes quality and innovation, particularly in lithography and etching processes. As a result, Japan has become a major player in the global market for electrostatic chucks.
How is South Korea’s semiconductor sector evolving in relation to electrostatic chucks?
South Korea’s semiconductors are growing fast, thanks to government support and tech investments. This growth means more need for electrostatic chucks. It’s a big opportunity for the country.
What are the key innovations in the U.S. concerning electrostatic chucks?
In the U.S., companies are making electrostatic chucks better for wafer processing. They’re working on new technologies and improving how they work. This is helping the U.S. stay competitive.

