$87.2 Billion Conventional Corn Seed Market Thrives by 2025: Brazil, U.S., and China Lead the Way
The global conventional corn seed market is a crucial part of the larger commercial seeds industry, which has a significant influence on farming practices worldwide. This market, valued at around USD 12.5 billion in 2025, is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.67% from 2025 to 2033.
- Last Updated:
Conventional Corn Seed Market Q1 and Q2 2025 Forecast
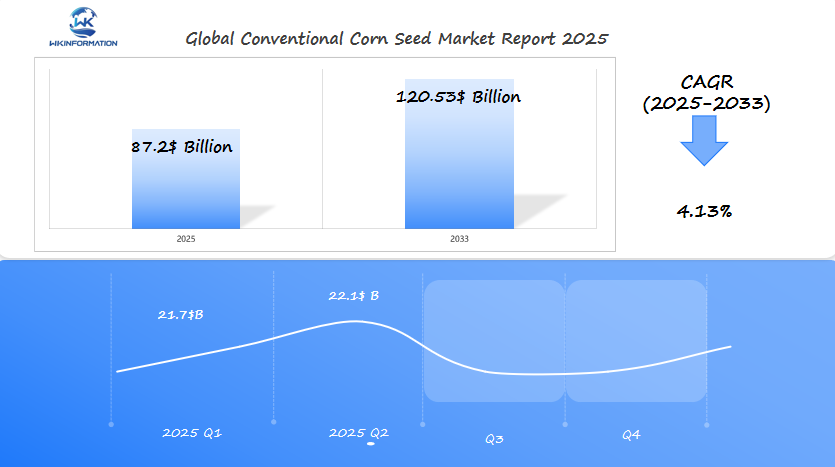
The Conventional Corn Seed market is expected to reach $87.2 billion in 2025, with a CAGR of 4.13% from 2025 to 2033. In Q1 2025, the market is projected to generate approximately $21.7 billion, driven by strong demand from Brazil, the U.S., and China, where corn continues to be a staple crop for animal feed, biofuel production, and food processing. The steady adoption of conventional seed varieties is linked to their proven performance in diverse climatic conditions and cost-effectiveness, particularly in regions with large-scale farming operations.
By Q2 2025, the market is expected to grow to $22.1 billion, with Brazil maintaining its position as one of the largest producers of corn due to favorable growing conditions and large agricultural land areas. China and the U.S. are also poised for continued growth, supported by increasing demand for ethanol production and livestock feed, as well as strong government support for agricultural development. The expansion of sustainable farming practices and increased focus on crop yields are anticipated to further boost the market.
Key Takeaways
- Market value to hit $87.2 billion by 2025
- Brazil, U.S., and China are top producers and exporters
- Non-GMO demand fuels growth in the corn seed market
- Climate resilience and yield improvements are critical priorities
- Sustainability drives innovation in seed development
Understanding the Upstream and Downstream Processes in Conventional Corn Seed Production
Every successful corn crop has a complex background. Corn seed production begins with research and hybrid development. Companies spend on labs and field trials to boost traits like pest resistance and yield. Soil nutrients and irrigation systems are also crucial at this stage.
Upstream Process: Research and Development
In the upstream process, key activities include:
- Research
- Breeding
- Sourcing raw materials
The main players involved in this stage are:
- Agricultural universities
- Seed breeders
Downstream Process: Processing and Distribution
In the downstream process, key activities include:
- Processing
- Packaging
- Distribution
The main players involved in this stage are:
- Seed retailers
- Logistics providers
Efficiency in both stages is key to corn seed production success. New technology and data analytics improve quality control, cutting waste. Farmers get reliable supplies, and consumers enjoy affordable, quality corn. This chain keeps food, feed, and biofuel sectors stable worldwide.
The Importance of Upstream Efficiency
In the upstream process, efficiency is crucial for several reasons:
- Improved research outcomes: By optimizing research processes, companies can develop new corn hybrids with desirable traits more quickly.
- Cost-effective breeding programs: Efficient breeding programs can lead to faster generation turnover, allowing for the selection of superior varieties in less time.
- Sustainable sourcing of raw materials: Streamlining the sourcing of raw materials such as seeds or genetic resources can reduce costs and ensure a steady supply for breeding activities.
The Significance of Downstream Efficiency
Similarly, efficiency in the downstream process has its own set of benefits:
- Timely processing: By minimizing delays in seed processing after harvest, companies can maintain seed quality and viability.
- Effective packaging solutions: Innovative packaging techniques can enhance shelf life and protect seeds during transportation.
- Streamlined distribution channels: Optimizing logistics operations ensures that seeds reach farmers promptly, enabling them to plan their planting schedules effectively.
By focusing on improving efficiency in both upstream and downstream processes, stakeholders in the corn seed industry can enhance overall productivity and meet the growing demand for corn globally.
Key Trends Driving the Conventional Corn Seed Market: Demand for Non-GMO and Sustainable Agriculture
More people want non-GMO crops because they care about what they eat. Farmers are listening, choosing seeds that are good for both people and the planet. They’re finding ways to grow food that’s healthy and doesn’t harm the environment.
- Increased use of organic farming methods to reduce chemical reliance
- Growing partnerships between seed companies and environmental groups
- Rising adoption of crop rotation to improve soil health
“Sustainability is no longer optional—it’s essential for long-term market viability.” —USDA Sustainable Agriculture Report, 2023
The U.S. Farm Bill is making farming greener. Big names like General Mills and Chipotle are choosing non-GMO crops. This makes seed producers work harder to offer more non-GMO options.
Climate change is also changing things. Farmers need seeds that can handle droughts and pests. This mix of sustainability and strong crops is the new normal in farming.
Challenges in Conventional Corn Seed Production: Yield Efficiency and Climate Resilience
Conventional corn seed production is facing big challenges. Farmers must meet growing demand while protecting the environment. They focus on getting the most from their land without harming it.
Climate changes like unpredictable weather and extreme temperatures are making things harder. These changes are pushing farmers to change their ways.
Key challenges include:
- Unpredictable weather patterns disrupting planting cycles
- Soil degradation from repeated monoculture farming
- Water scarcity in arid regions like the U.S. Midwest
“Climate resilience isn’t just about survival—it’s the foundation of future food systems,” said Dr. Lena Torres, an agronomist with the USDA Climate Hub.
Sustainable agriculture is a solution to these problems. Practices like cover cropping and precision irrigation help keep soil moist and reduce chemical use. New seed varieties, like Pioneer’s drought-tolerant hybrids, are being developed.
Small-scale farmers in Brazil are using intercropping. This method increases biodiversity and yields. It shows that sustainable farming can work.
Overcoming these challenges needs teamwork. Seed companies, governments, and farmers must work together. By focusing on long-term soil health, we can ensure food for the future.

Geopolitical Influence on the Conventional Corn Seed Market
Trade policies and international agreements shape where corn seeds are grown and sold. Market leaders like the U.S., Brazil, and China face constant shifts in global politics that directly impact their seed industries.
- Trade barriers between nations can delay seed exports and imports.
- Climate resilience research funding often aligns with geopolitical alliances.
- Regulations on seed patents and GMO use vary by country, affecting global supply chains.
When countries focus on climate resilience in agriculture, they attract partnerships with seed companies. For example, Brazil teams up with U.S. firms on drought-resistant hybrids. On the other hand, China’s policies support local research to cut down on foreign seed imports. These moves show how national goals guide innovation.
Political tensions over food security lead governments to invest in local seed production. Farmers in Africa now use climate-resilient varieties thanks to international aid. These programs rely on global alliances for funding and sharing technology.
Types of Conventional Corn Seeds: Dent, Flint, and Sweet Corn Varieties
Conventional corn varieties are key in global farming. Farmers pick from three main types: dent, flint, and sweet corn. Each type has special traits for different uses.
- Dent corn: Its dented kernels make it a field crop leader. It’s used in animal feed, processed foods, and biofuels.
- Flint corn: Its hard kernels help it survive dry climates. It’s great for popcorn and polenta.
- Sweet corn: High in sugar, it’s perfect for eating fresh. It’s grown a lot in the U.S. and sold worldwide.
| Type | Key Traits | Primary Uses |
| Dent | Soft starch, high yield | Animal feed, processed snacks |
| Flint | Hardy, drought-tolerant | Popcorn, human food |
| Sweet | Sugary kernels | Fresh market, canning |
Choosing the right conventional corn varieties depends on many factors. Climate, market demand, and farming goals are important. Dent corn’s versatility and flint corn’s toughness are big reasons for their popularity. Sweet corn’s taste is a big hit in the food world. Farmers and buyers use these differences to boost their success.
Applications of Conventional Corn Seeds in Food, Animal Feed, and Biofuel Production
Conventional corn seeds are key to three big industries. In food, they turn into cornmeal, corn syrup, and snacks. For animal feed, ground corn helps raise livestock, supporting meat and dairy.
Biofuel production turns starch into ethanol. This renewable energy powers cars and cuts down on fossil fuel use.
1. Food Production
Conventional corn seeds are processed into various food products for global markets. These include:
- Cereals
- Tortillas
- Sweeteners
2. Animal Feed
Ground corn from conventional seeds provides essential carbohydrates for livestock such as poultry, pigs, and cattle.
3. Biofuel Production
Ethanol plants play a crucial role in converting corn into fuel to meet U.S. renewable energy targets. Companies like Archer Daniels Midland and POET operate these plants across the country.
“Corn-based ethanol reduces carbon emissions by 40% compared to gasoline, driving America’s clean energy transition.” – U.S. Department of Energy, 2023
Biofuel production needs corn rich in starch. The Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) requires ethanol in gasoline, boosting demand for corn seeds.
This policy creates an $8 billion market for corn-based biofuels every year.
Using corn for biofuels creates jobs and helps rural areas. New seed genetics improve starch content, making yields better for food and energy. Farmers and energy companies work together to be sustainable and productive.
Global Insights into the Conventional Corn Seed Market
Global agriculture trends show a mix of chances and hurdles across the world. North and South America lead in production, but Africa and Asia-Pacific are growing fast. Farmers in these areas want seeds that are affordable and work well in their climates.
| Region | Market Growth Rate (%) | Key Focus |
| Asia-Pacific | 5.2 | Smallholder farmer support |
| Africa | 4.8 | Climate-smart seed varieties |
| Europe | 3.1 | Sustainable practices |
Emerging countries are teaming up with seed companies like Corteva and Syngenta. For example, Kenya’s maize yield jumped 18% in 2023 with new drought-resistant seeds. This shows how global innovation in farming can help different areas.
“Collaboration between governments and agribusinesses is key to scaling solutions for small-scale farmers.” – Dr. Elena Marquez, International Crop Research Institute
Markets in Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe are also growing. This is thanks to new policies and more demand for biofuels. As global agriculture changes, sharing data and seed banks will be vital for keeping farming productive everywhere.
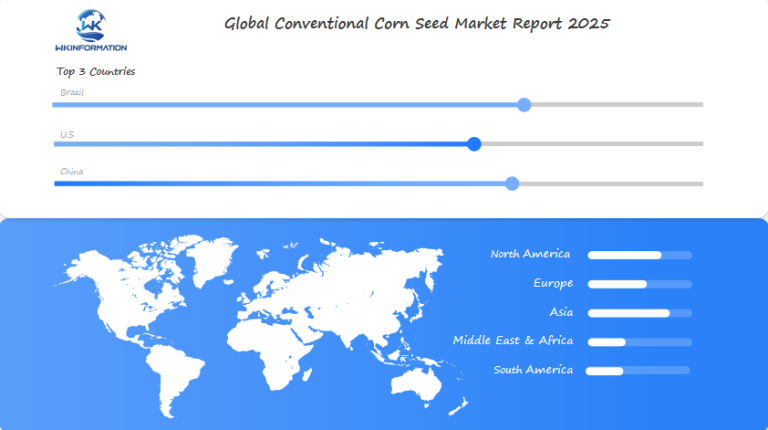
Brazil’s Leadership in Conventional Corn Seed Exports and Hybrid Innovations
Brazil is the top exporter of conventional corn seeds in the world. It utilizes hybrid innovations specifically designed for tropical climates. These seeds enable farmers to increase their yields and combat diseases, making them highly sought after globally.
Organizations like Embrapa collaborate with farmers to develop seeds that thrive in various soil types and weather conditions. As a result of these hybrid innovations, Brazil now exports corn to over 40 countries and has become the second-largest corn exporter worldwide.
Key Factors Behind Brazil’s Success
Several factors contribute to Brazil’s success in the corn seed industry:
- Adapted hybrids have been shown to boost productivity by up to 30% in challenging agricultural conditions.
- Partnerships with global agribusinesses ensure that improved seed varieties are widely adopted by farmers.
A Blend of Tradition and Technology
Brazil combines traditional farming practices with modern technology. Farmers leverage data analytics to optimize their planting decisions and incorporate locally bred hybrids into their cultivation methods. This approach not only reduces costs but also promotes sustainable agricultural practices, which is why Brazilian seeds are favored by farmers in Africa and Asia.
Future Goals: Leading in Hybrid Research
Brazil aims to maintain its leadership position in hybrid research. By 2025, the country has set a goal to introduce drought-resistant seeds, which will play a crucial role in ensuring food security for all, particularly in the face of climate change challenges.
The U.S.’s Role in Large-Scale Farming and Seed Technology Advancements
The U.S. is at the forefront of seed technology advancements, which are crucial for the progress of large-scale farming. Companies such as Corteva Agriscience and Bayer Crop Science are making significant investments in research aimed at enhancing crop resilience and increasing yields.
Their primary focus is on developing crops that can withstand drought conditions and resist pests, which will have a direct positive impact on corn production.
seed technology
- Genetic research programs at universities like Purdue and Iowa State drive breakthroughs.
- Automation in planting and harvesting cuts costs, aiding farmers.
- Partnerships with tech firms integrate data analytics into seed development.
Modern seed technology tools help farmers monitor soil health and climate impacts. Precision planting systems use GPS to place seeds perfectly, saving resources. These tools are now common on 75% of U.S. corn farms, as reported by USDA 2023 data.
| Year | Corn Production (million bushels) | Seed Tech Adoption |
| 2020 | 15,500 | 68% |
| 2021 | 16,000 | 72% |
| 2022 | 14,800 | 75% |
Advances in seed technology keep U.S. farms competitive. Innovations like drought-resistant hybrids help crops survive climate changes. This technology supports both domestic food production and exports, solidifying the U.S. as a global agriculture leader.
China’s Growing Demand for Conventional Corn Seed in Food Security Initiatives
China is focusing on food security and sees conventional corn seed as key. The 14th Five-Year Plan aims to boost corn production to cut down on imports. Farmers and scientists are using high-yield conventional varieties to achieve this.
Key strategies include:
- National subsidies for seed R&D and farmer adoption
- State-owned seed banks preserving over 50,000 corn varieties
- Public-private partnerships with companies like Pioneer Hi-Bred
Experts say hybrid seeds are vital in dry areas. A 2023 report by the China National Grain and Oils Information Center shows a rise in corn yields. Yields have gone up 8% since 2020 thanks to these efforts.
| Year | Target Yield (Metric Tons) |
| 2023 | 275 million |
| 2025 | 310 million |
| 2030 | 350 million |
These plans match the National Food Security Strategy (2023-2030). It focuses on growing staple crops on its own. By 2030, China wants to supply 98% of its corn needs, up from 92% in 2022. This shows how important conventional corn is for food stability, especially with climate changes.
The Future of Conventional Corn Seed: Climate-Resilient and Drought-Tolerant Varieties
Climate change is changing how we farm. Drought-tolerant varieties are key to new ideas. Scientists and seed companies are working fast to make corn that grows well in dry places. This could help farmers in areas where water is scarce.
New ways to breed corn, like CRISPR, help find traits that handle heat and dryness. Companies like Corteva Agriscience and Syngenta are testing these traits. They want to keep yields high even when it’s dry.
Farmers in the U.S. and Brazil are trying these new seeds. They want to see if they can keep crops growing even when it doesn’t rain for a long time.
| Benefit | Impact |
| Water Efficiency | Reduces irrigation needs by up to 30% |
| Yield Stability | Maintains 85% of typical yields in droughts |
| Adaptability | Suits both small farms and industrial-scale operations |
These drought-tolerant varieties also help the planet. By 2030, they could be used on 40% of U.S. cornfields, a USDA report says. Now, partnerships are funding tests in the Midwest to see how they do in real life.
Developers say these new seeds are not just for survival. They can also make farming more profitable. Farmers who tried these seeds saved 15-20% on water and fertilizers. Soon, these seeds will be common in places like California and Texas, where water is very scarce.
Competitive Landscape in the Conventional Corn Seed Market
- Bayer CropScience AG – Monheim am Rhein, Germany
- Corteva Agriscience – Wilmington, Delaware, USA
- Syngenta Group (ChemChina) – Basel, Switzerland
- BASF SE – Ludwigshafen, Germany
- Monsanto Company – St. Louis, Missouri, USA
- Limagrain Group – Saint-Beauzire, France
- DLF Seeds A/S – Roskilde, Denmark
- Pacific Seeds – Toowoomba, Queensland, Australia
- Nuziveedu Seeds Ltd. – Hyderabad, Telangana, India
- China National Seeds – Beijing, China
Overall
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Global Conventional Corn Seed Market Report |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Segment by Type | · Dent Corn (Zea mays indentata)
· Flint Corn (Zea mays indurata) · Sweet Corn (Zea mays saccharata) |
| Segment by Application | · Food Production
· Animal Feed · Industrial Uses |
| Geographies Covered | · North America (United States, Canada)
· Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Russia) · Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan) · Southeast Asia (India) · Latin America (Mexico, Brazil) |
| Forecast units | USD million in value |
| Report coverage | Revenue and volume forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
The global conventional corn seed market is expected to hit $87.2 billion by 2025. This growth shows how innovation and demand work together. Countries like Brazil, the U.S., and China lead the way, using new hybrid seeds and big farms to boost production.
Dent corn is used in food, while flint corn goes into animal feed. Each type is crucial for keeping farms healthy.
Sustainability and climate resilience are changing the market outlook. Companies are focusing on seeds that can handle drought and are non-GMO. Trade policies and global politics affect supply chains, but partnerships between farmers and tech experts are finding ways to overcome yield issues.
China and Brazil are pushing for food security, showing how local needs shape global trends. This affects how corn is grown and used worldwide.
The market outlook looks good as research on climate-smart seeds speeds up. Finding a balance between old farming ways and new tech will be crucial. The goal is to meet growing demand while protecting the environment.
This industry’s success depends on working together. It’s about growing sustainably, using resources wisely, and keeping food stable for everyone.
Global Conventional Corn Seed Market Report (Can Read by Free sample) – Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Conventional Corn Seed Market Analysis Overview
- Competitive Forces Analysis (Porter’s Five Forces)
- Strategic Growth Assessment (Ansoff Matrix)
- Industry Value Chain Insights
- Regional Trends and Key Market Drivers
- Conventional Corn SeedMarket Segmentation Overview
Chapter 2: Competitive Landscape
- Global Conventional Corn Seedplayers and Regional Insights
- Key Players and Market Share Analysis
- Sales Trends of Leading Companies
- Year-on-Year Performance Insights
- Competitive Strategies and Market Positioning
- Key Differentiators and Strategic Moves
Chapter 3: Conventional Corn Seed Market Segmentation Analysis
- Key Data and Visual Insights
- Trends, Growth Rates, and Drivers
- Segment Dynamics and Insights
- Detailed Market Analysis by Segment
Chapter 4: Regional Market Performance
- Consumer Trends by Region
- Historical Data and Growth Forecasts
- Regional Growth Factors
- Economic, Demographic, and Technological Impacts
- Challenges and Opportunities in Key Regions
- Regional Trends and Market Shifts
- Key Cities and High-Demand Areas
Chapter 5: Conventional Corn Seed Emerging and Untapped Markets
- Growth Potential in Secondary Regions
- Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Chapter 6: Product and Application Segmentation
- Product Types and Innovation Trends
- Application-Based Market Insights
Chapter 7: Conventional Corn Seed Consumer Insights
- Demographics and Buying Behaviors
- Target Audience Profiles
Chapter 8: Key Findings and Recommendations
- Summary ofConventional Corn SeedMarket Insights
- Actionable Recommendations for Stakeholders
Access the study in MULTIPLEFORMATS
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1-866-739-3133
Email: infor@wkinformation.com
What is the projected growth of the conventional corn seed market by 2025?
The conventional corn seed market is expected to grow to $87.2 billion by 2025. This growth is led by countries like Brazil, the United States, and China.
How do upstream and downstream processes affect corn seed production?
Upstream processes involve seed development and improving production efficiency. Downstream processes handle distribution and sales. Together, they form a crucial part of the supply chain.
What trends are shaping the demand for conventional corn seeds?
The demand for non-GMO crops is increasing. This is due to consumer preferences and policies supporting sustainable agriculture.
What challenges does the conventional corn seed market face?
The market faces challenges like improving yield efficiency and adapting to different climates. These are essential for climate resilience in production.
How does geopolitical influence affect the corn seed market?
Geopolitical factors such as trade policies and international relations have an impact on the corn seed market. They play a role in shaping production, distribution, and innovation within the conventional corn seed market.
What are the different types of conventional corn seeds available?
There are mainly three types of conventional corn seeds: dent, flint, and sweet corn. Each type has its own uses and characteristics in agriculture.
In which sectors are conventional corn seeds used?
Conventional corn seeds are used in food production, animal feed, and biofuel. They are versatile and benefit various industries.
What global insights are relevant to the conventional corn seed market?
The market varies by region, with emerging markets and competitive dynamics playing a role. This gives a full view of the market’s growth across continents.
What role does Brazil play in the global corn seed market?
Brazil leads in corn seed exports and has innovated in hybrid seeds. It stands out in the global agricultural scene.
How has the U.S. contributed to advancements in seed technology?
The U.S. supports large-scale farming and seed technology innovation. It is a leader in the conventional corn seed market.
How is China’s focus on food security influencing the corn seed market?
China’s focus on food security boosts demand for conventional corn seeds. This drives strategies to address food production challenges.
What is the future outlook for conventional corn seed varieties?
The future looks promising for conventional corn seed varieties, with ongoing research and technology driving the development of seeds that are climate-resilient and drought-tolerant.
What does the competitive landscape look like in the conventional corn seed market?
The corn seed market is competitive, with many major players. They use innovation and strategic investments to stand out.

